Leverage means you are borrowing capital to control larger trading positions with minimal capital. While a risky tool, leverage when managed successfully can amplify your profits when trading CFD financial instruments. In this guide, we’ll explore what leverage is, how to calculate your leverage and how to apply it. We will also what leverage Forex brokers can offer in the UK since the FCA place some leverage limitations.
What is Leverage in Forex Trading?
Leverage in forex trading allows a trader to take a small amount of capital, and control a larger position size in their desired currency. Doing this can magnify the size of both their profits and losses. You might also hear leverage trading referred to as margin trading. For example, a forex trader might have 1000 Australian Dollars in their trading account. Using their forex broker’s 100:1 leverage facility, they purchase $100,000 of the AUDUSD currency pair.
Now the trader controls a position size that is 100 times the capital in their account, if the AUDUSD rate climbs 1%, they will make a 100% return on their trading position. But, if the AUDUSD rate falls by 1%, the trader will lose 100% of their capital.
Making losing trades is a part of forex currency trading, just as it is when trading CFDs, stocks, and futures. So, it’s important for each trader to consider their risk tolerance, trading skill, market experience, and the volatility of their chosen forex trading strategy before electing to use high leverage with their trades.
It’s also important for all traders, from absolute beginners, to highly advanced, to use risk management tools and strategies, such as stop-loss orders and position-sizing tactics before entering their trades.
How Leverage Works in Forex Trading
Now, that it’s clear that leverage is a powerful tool that can magnify both your potential profits and losses in trading, let’s look at how leverage works with regulated forex brokers.
Each forex broker will have a leverage ratio that they offer to clients when trading with CFD financial instruments. The maximum leverage the broker is permitted to allow their clients will be determined by the broker’s regulator (assuming the broker has one). For a broker to legally offer trading services in the UK, the broker must hold a license from the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) which regulates the financial services industry across England, Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland.
The FCA allows brokers to offer a maximum of 30:1 for major Forex pairs and 20:1 for minor and exotic Forex pairs for retail traders. They also allow brokers to offer leverage of 500:1 for traders that meet the conditions to trade using a Professional Account.
The maximum leverage for retail traders with other financial products includes 20:1 for Gold and major stock indices, 10:1 for other commodities (I.E. silver), and 5:1 for stocks. The FCA does not permit cryptocurrency trading unless you have a Professional Account.
As a client of the forex broker, you will be asked to deposit a certain amount into your forex trading account, and this deposit will then be able to be used as a trading margin. For example, if you deposit $500 into a forex broker that allows you 100:1 in financial leverage, you will have $500 in margin and will be able to purchase a trading position as large as $50,000.
Should you go and max out your use of leverage as soon as you open your Forex account? Absolutely not, as a smart trader, you should rarely be maxing out leverage on your entire trading margin.

Selecting Leverage Trading Levels
When trading in forex market, selecting an intelligent leverage level is one of the simplest, yet most important things that will help you to be successful.
To determine the right leverage level for you, it’s a good idea to consider how much your risk tolerance level is, the amount of trading capital you have, your experience in trading markets, and the volatility levels of your chosen forex trading strategy.
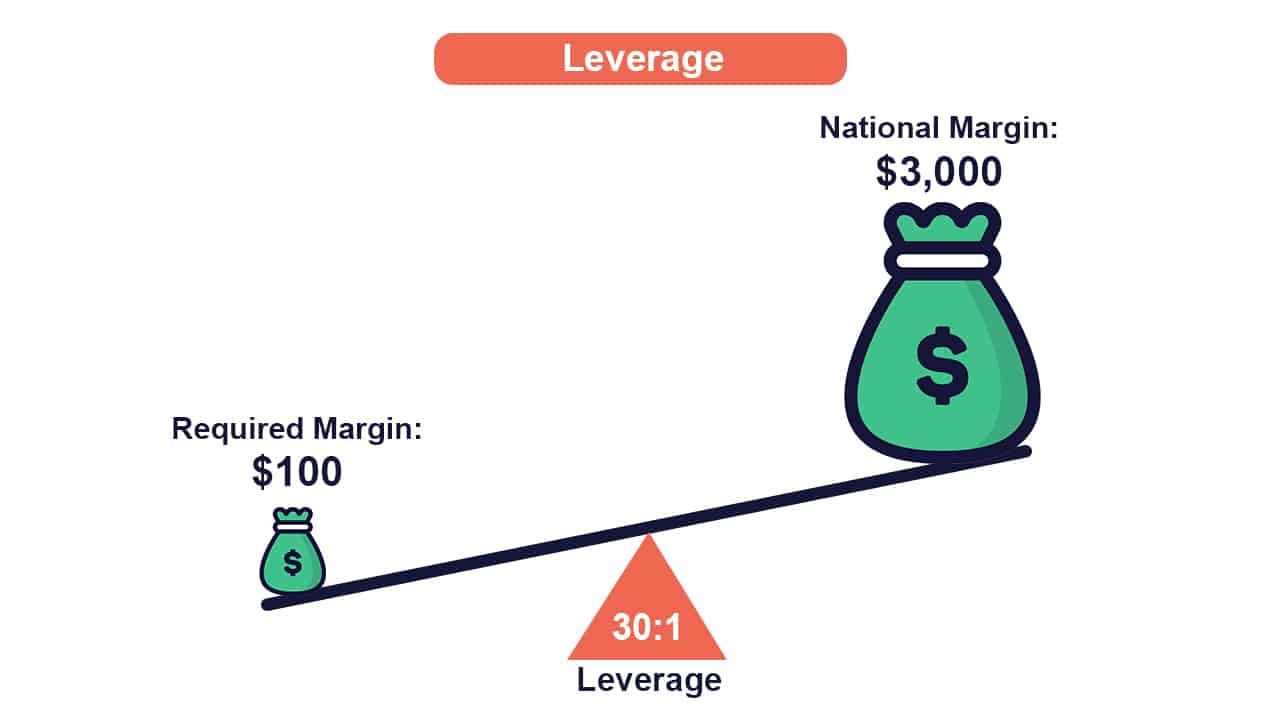
Many traders elect to risk a certain percentage of their trading capital on each trade. For example, a trader might have $20,000 in total capital, and be comfortable risking 2% of it on each trade, meaning they are comfortable with losing $400 on a trade.
Let’s assume that this trader has a strategy that risks 50 pips on each trade, meaning that they want to take a position where each pip is worth $8. This trader simply needs to use a leverage amount that allows them to take a trading position that’s worth $8 for each pip.
Low vs High Leverage
When it comes to forex trading, the usage of leverage can either be highly profitable, or incredibly destructive for your trading capital.
Leverage is essentially taking a small amount of your own money, and borrowing the rest, to take a large position size in your chosen currency. If the currency moves in your favour, it can be highly profitable, if the exchange rate moves the other way, you can say goodbye to your trading capital.
To determine whether to use high or low leverage, you should ask yourself a few things:
- How comfortable are you losing the trading capital in your account?
- Are you relying on your trading for a consistent income? Do you have another source of income?
- Does your trading strategy have lots of losing trades, or large-size losing trades?
- How’s your trading psychology? Can you keep your head together after taking some losses, and keep making intelligent trades?
Basically, selecting the right leverage ratio comes down to how much capital you have, and how much you’re looking to risk on each trade.
If you’re risk averse, or looking to make a living from your trading capital, you’ll probably want to use smaller amounts of leverage, and risk smaller amounts each trade.
Alternatively, if you’re using your forex account to make a side income, and perhaps get a little thrill from the wins and losses, you may elect to use a higher leverage ratio.
Optimal Leverage Based On Trading Styles
Different forex trading styles require different risk management techniques and different leverage levels.
For example, Best Brokers for Scalping, the types of traders who do very quick in and out trading, often use higher leverage amounts, as they’re trying to make profits from very small movements in their chosen currencies. On the other hand, longer-term position traders will often use smaller amounts of leverage, as they are looking to profit from larger, long-term moves in various currencies.
Generally, spread betting is more short term (as there are overnight fees) and requires a spread betting UK trading platform< to trade with leverage for this unique trading style.
Managing Risk with Leverage
Leverage can be a powerful tool, increasing the size of both your potential profits and losses. Selecting the right leverage amount is a function of your risk management plan. All traders should have a well-thought-out risk management plan before even entering their first forex trade.
A risk management plan includes how much you will risk per trade, where you will exit a losing trade, how much you will look to profit on winning trades, and how you will protect your trading capital from large losses.
Let’s take a look at the two most important risk management concepts, stop-loss order, and position sizing:
1. Stop-Loss Orders
Stop Loss Orders are essential for managing your risk, no matter if you are trading CFDs, forex, stock, or futures.
Using a stop-loss order tells your broker to exit your trade, at a particular level, usually when the trade is losing money. A take profit is the opposite, it tells your broker to exit your trade when a particular profit level is reached.
For example, if you enter a long EURUSD trade at 1.08, and place a stop-loss order at 1.07, at any point in time, if the EURUSD rate drops to 1.07, your broker will quickly exit your position, preventing you from losing any more money.
Selecting the right stop-loss point depends on how much capital you’re looking to risk on each trade, and how many pips of risk are required by your trading strategy on each trade.
For example, a scalper might risk 5-10 pips, looking to make a profit on a 10 or 20 pip move in the next few minutes or hours. They will set a stop-loss at 5-10 pips from their entry price.
A long-term position trader may look to risk 300 pips, looking for a move over the next month of 1000-2000 pips. The position trader would look to place their stop-loss 300 pips from their entry price.
2. Position Sizing
Position sizing is a risk management technique that consists of determining the volume to be bought or sold on a currency pair based on your strategy.
For example, if you have $100,000 in trading capital, and you are looking to risk 2%, or $2,000 of it on an AUDUSD trade. Let’s assume that your strategy risks 100 pips to make 300 pips profit.
In this example, you would be looking to risk $20 per pip, which is a position size of $200,000 (1:2 leverage assuming you keep all of your capital in your account).
To determine the right position size, you should first know what percent of capital you are looking to risk on each trade. As a rule of thumb, most serious traders will risk anywhere from .5% to 5% of their capital on each trade.
Calculating Leverage When Trading
Now that you have an idea of how important it is to determine your risk levels and use appropriate leverage amounts in your forex trading, now let’s take a closer look at how to calculate leverage and margin levels.

Here are the simple formulas that will allow you to calculate leverage and margin by hand. If you’re not a math person, don’t worry, most trading platforms will have tools to do this for you, but it’s always good to know how the numbers work.
Leverage Calculation Formula
In order to calculate leverage on a forex position, first you need to know these two things:
- The value of your open trade
- The forex broker margin requirement for your chosen currency pair
With these two factors, you can now simply input them into the following formula:
Leverage = (Trade Value / Margin Requirement)
For example, you want to purchase 100,000 GBP/USD. Your brokerage account requires a 2% margin on GBP/USD trades. The current exchange rate for GBP/USD is 1.2.
The value of your trade is £100,000 x 1.2 = £120,000.
Your broker requires a 2% margin = £120,000 x 2% = £2,400.
Now, we input them into the original formula.
Leverage = (£120,000 / £2400)
Leverage = 50:1
Margin Calculation Formula
Now, let’s use some simple mathematics to calculate how much margin is needed for a trading position.
To do this, we first need to know:
- The value of the trading position
- The leverage ratio of the currency in your brokerage account
With these two factors, we can plug them into the margin calculation formula:
Margin = Trade Value/Leverage Amount)
We’ll use a similar trade to the last calculation. We want to purchase 100,000 GBP/USD. Our brokerage account offers 50:1 leverage on GBP/USD trades. The current exchange rate for GBP/USD is 1.2.
The value of our trade is £100,000 x 1.2 = £120,000.
The leverage ratio on GBP/USD is 50:1.
So, we can determine margin with this formula:
Margin = (£120,000 / 50)
Margin = £2,400
Once again, maybe you slept through high school math and you’re starting to fall asleep once again. Don’t worry, your trading software will probably do a lot of this for you, but it’s always good to know how these numbers work. Overall thought, picking the best forex brokers in UK is the key to helping manage leverage effectively.
Leverage in Other Financial Markets
In the world of financial markets, leverage isn’t exclusive to just forex trading. Leverage is also used in other financial markets, such as the stock market, futures markets, cryptocurrencies, options, and bonds.

Similar to forex trading, leverage in other financial products allows traders or investors to increase their exposure to financial products, increasing the size of potential gains and losses.
Let’s take a quick look at how leverage works in some of the other major financial asset classes.
1. Stock Market Leverage
Stock market leverage enables investors to hold a larger amount of stock compared to the amount of capital they have in their brokerage account. This is done by using their capital for margin and borrowing the rest of the funds to purchase stocks.
This type of borrowing to buy stocks is often done by a margin lending facility attached to a stock brokerage firm.
Alternatively, traders can also leverage into stock positions by using CFDs. With individual stock CFDs, the trader will be able to take a large position in an underlying stock compared to their trading capital and benefit from upside movements in the stock price.
2. Futures Market Leverage
Futures contracts are a type of financial contract between a buyer and seller, that obligates them to make a trade on a future date, at an agreed price.
There are futures contracts that cover a huge amount of financial and commodity products, these range from the Best Brokers for Gold CFD Trading to the EURUSD, to copper, to the S&P500 index, to Bitcoin and so many others.
Companies such as investment firms, agricultural producers and gold mining operations use futures contracts to hedge price exposure, protecting from adverse moves and sometimes even profiting from positive moves in the price of various assets.
For individual retail traders, futures contracts are often used as a simple way to place trades speculating on the price of underlying assets, such as the value of the S&P500 index.
For example, take the ES futures contract, traded on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange, which mirrors the underlying price of the S&P500. For every tick the futures contract moves (a tick is similar to a pip in forex, the minimum amount the contract can move), the futures contract will gain or lose in value $12.5.
So, if you purchase an ES futures contract, and the price moves 200 ticks in your favour, you will make $2500.
And how much margin did you need to deposit to buy a single futures contract? If you’d traded with a broker, you would’ve needed just $8,600 in your account.
Conclusion On Leveraged Trading
If you want to succeed in trading forex, you want to make sure that you’re able to use leverage intelligently. Leverage can help you to make large returns on a small amount of capital, but it can also cause you to lose huge amounts or even the entire amount that you have in your trading account.
Intelligently using leverage has a lot to do with the risk management plan, how much capital you’re willing to risk on a losing plan, and how strong your trading plan is, amongst many other factors. We recommend you compare forex brokers based on their features, including leverage, to ensure they meet your specific needs.
FAQs
What is a good leverage ratio for forex?
Determining a good leverage amount for your forex trading strategy has a lot to do with how much you’re willing to risk on a losing trade and how much of your trading capital you wish to keep in your account.
If you can tolerate a lot of risk and want large wins and losses, you might want to use a high leverage amount.
On the flip side, if you’re trying to make a living trading forex, and looking for steady consistent gains, you’ll want to risk a small amount of capital and use small amounts of leverage.
What does 1 to 500 leverage mean in forex?
When it comes to forex trading, 1:500 leverage offers traders the chance to control a currency position that is 500 times the size of the margin capital they’ve deposited in their account.
With that level of leverage, if your total position moves 1%, you’ll make a staggering 500% return on your margin capital.
But, there’s a major downside as well. If your trading position loses just 0.2%, a small fluctuation, you’ll lose 100% of your risk capital.
What is leverage in trading?
Using a small amount of capital in a forex brokerage account, a trader can control a much larger position size by borrowing the extra amount from their forex broker.
This has the effect of allowing for large returns on capital in the account, as gains are amplified. But also comes with the risk of huge losses if the trader places losing trades.


