Forex trading is a multi-billion dollar industry, and brokers are crucial in connecting buyers and sellers. Understanding how brokers make money helps you to choose the right broker for your trading needs and goals. This guide covers the different types of forex brokers, including ECN and market makers, and how they make money through spreads, commissions, and other fees such as deposit/withdrawal fees, inactivity fees, and premium features.
1. ECN Brokers vs Market Makers
One of the most common questions new traders ask us is, “Should I trade with an ECN forex broker or a market maker?”
Let’s start by reviewing the difference between the two broker business models and whether they implement a No Dealing Desk Brokers that executes your trades.
ECN (Electronic Communications Network)
The first business model we want to go over is the ECN forex broker.
ECN is essentially a real-time connection between yourself and other participants within the forex market. These could be:
- Banks
- Financial institutions
- Hedge Funds
- Other traders
 True ECN forex brokers offer traders direct access to the best bid and ask prices, with no interference from a middleman. So during peak trading volume, the best bid and ask prices offered by multiple participants in the interbank market may be the same and therefore display a spread of zero!
True ECN forex brokers offer traders direct access to the best bid and ask prices, with no interference from a middleman. So during peak trading volume, the best bid and ask prices offered by multiple participants in the interbank market may be the same and therefore display a spread of zero!
To compensate for these extremely tight spreads, ECN forex brokers make money by adding a small commission charge to each trade.
While ECN accounts are favoured by styles such as high-volume traders who scalp or run automated systems that require razor-thin spreads, it’s worth remembering that spreads are still at the mercy of the forex market. If there’s no price available due to volatility or market hours, then the spread will not be zero.
You can be assured, however, that there is zero conflict of interest between the trader and an ECN forex broker. They want you to make money because they aren’t setting the prices and instead taking a commission on each trade. If you’re making money, you’re trading more volume and, therefore, paying more commissions.
A symbiotic relationship between the forex broker and trader!
STP (Straight-Through Processing)
The second business model in operation is the STP forex broker.
As a no-dealing-desk model, STP differs slightly from the true ECN model explained above.
STP forex brokers route client orders to liquidity providers who quote bids and ask prices.
With liquidity providers having a plethora of quotes, the STP forex broker will aggregate these to ensure you receive the best price possible, but with a spread markup added.
For example:
EUR/USD bid/ask prices from a liquidity provider
- 1.1000/1.1001.
EUR/USD bid/ask prices after STP forex broker markup
- 1.0999/1.1002.
When trading forex on an STP account with your broker, you’ll see a spread of 3 pips rather than 1.
With an STP forex broker, you’re trading against other participants in the market, not the retail forex broker themselves. It is essential because, like the ECN model, this ensures no conflict of interest. The broker wants you to succeed because they make money on the spread markup added to every trade, not because they take your losses.
Another example of a symbiotic relationship between the forex broker and trader.
Market Maker
The third and final business model is that of a market maker forex broker.
Market makers are forex brokers who operate a dealing desk to execute orders. They make a market for their clients, creating bid and ask prices for liquidity and matching buy orders with sell orders already on their book to minimise risk.
They simply become the counterparty to their clients’ positions by taking the other side of the trade.
Forex brokers who are market makers make money through spreads and by betting against their clients’ positions. This conflict of interest is why many traders find it hard to trust market makers, even if these fears are often unfounded.
The one big positive of market makers is that they’re the only forex broker able to offer fixed spreads to traders.
It all depends on what you’re looking for in a forex broker.
2. Spreads
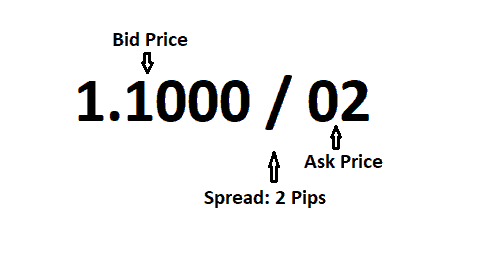 Now we understand the different types of forex brokers, let’s move on to the different types of charges that forex brokers use to make money.
Now we understand the different types of forex brokers, let’s move on to the different types of charges that forex brokers use to make money.
The first key charge that forex brokers use to make money is through their spreads:
Bid price: The price quoted for selling a currency pair.
Ask price: The price quoted for buying a currency pair.
Spread: The difference between the bid and ask price and the cut that the broker takes on your position.
If your trading platform displayed EUR/USD at 1.1000/1.1001, the quote would indicate a spread of 1 pip.
Depending on the business model that your forex broker has implemented, spreads can be fixed or variable. Both types of spreads have advantages and disadvantages, depending on the type of trader that you are.
We go over the two different types of spreads below.
Fixed Spreads
If your forex broker offers fixed spreads, you’re guaranteed that the price displayed on your trading platform will be the price you will have your trade executed.
Fixed spreads are often only offered by forex brokers who make their money as market makers.
Variable Spreads
If your forex broker offers variable spreads, the spread you see will change depending on current market conditions.
At times of high market liquidity such as the London open, you may see extremely tight spreads, sometimes as low as zero. At times of major news releases, on the other hand, the spread can widen as market participants pull their orders.
ECN and STP forex brokers usually offer variable spreads. As you can see, trading with each broker type, including brokers with best spread betting platforms UK can be both a blessing and a curse. While you may not notice any price manipulation by your ECN broker, you’re entirely at the whim of the market. Something that can be cut out if you trade with a market maker.
3. Commissions
The next key charge that forex brokers use to make money is through commissions charged to traders when they open and close orders.
ECN forex brokers often charge commissions to ensure they can still make money on trading accounts with spreads as low as zero. They aren’t running a charity, after all!
Due to the intense competition between forex brokers, commissions tend to be relatively low. Just check out Pepperstone’s commissions.
Pepperstone’s ECN Razor Account (per standard lot):
- $3.50 trade entry.
- $3.50 trade exit.
Using the Pepperstone example, this means that you’ll be charged $3.50 per leg. That’s $3.50 on the entry leg and then $3.50 more on the exit leg of your trade.
Each trade makes $7.00 total to open and close one standard lot position in any currency pair. This is known as a round turn, and the razor-thin spread quoted is your total charge for that trade.
Remember that these commission charges are pro-rated according to your position size. Not everyone trades one standard lot per trade, so you’ll be charged accordingly.
Compare Pepperstone vs IC Markets commission charges by clicking that link and checking out the full comparison table of our two highest-rated ECN forex brokers. See our full Pepperstone Review for more details.
4. Other Fees
The final charges that you need to consider when answering the question of how forex brokers make money are those placed under the ‘other’ category.
These other fees aren’t related to your CFD trading but rather all the extras required for it to happen. They can differ significantly from broker to broker, and most are entirely optional extras for traders looking for that little extra edge.
Let’s take a look at some of the big ones here now.
Deposit/Withdrawal Fees
You may be charged a fee depending on how you fund your account.
The thing here is that these fees often come from the bank or payment provider and are not making the broker money.
Here are a few of the most popular deposit/withdrawal methods and a look at some of the fees you may be charged:
Bank wire transfer: If you’re using a foreign bank to where your broker is situated, they may charge transfer or service fees. This is not your broker trying to make money but just the cost of using the inefficient global banking system.
Credit/debit card: Credit card providers such as Mastercard or Visa may charge a transaction fee whenever you use funds on a card to fund your account. International currency fees may also apply if your account is in a different denomination than your card.
Payment services (Skrill etc): Traders who don’t want to use their bank account or cards often choose third-party payment services such as Skrill or Neteller. While they facilitate the under-banked population, they’re also much more expensive than if you used either of the previous 2 methods.
Inactivity Fees
Your account with a forex broker can’t be used as a regular bank account to store your funds.
If you leave your trading account funded but don’t trade for a certain period, your broker will most likely charge an inactivity fee.
An inactivity fee is usually a monthly or quarterly charge that is applied to your account if there has been no trading activity for over 12 months. Again, the times and charges will vary from broker to broker.
How to avoid inactivity fees:
- Place a trade on your account.
- Your account balance reaches zero.
- Close your account.
While inactivity fees aren’t exactly how forex brokers make their money, they’re worth watching so you don’t get caught out.
Trading Platform Extras
Most forex brokers offer all clients the MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, and cTrader platforms free of charge. But some brokers also provide additional features and add-ons you may need help finding on the standard version.
Additional trading platform extras may include:
- Risk management tools.
- Trading journals.
- Automated trading.
- Trade management tools.
You should also check out the broker we’ve reviewed as having the best forex trading platform – Axi. Our Axi review provides more details on their offerings, including a ton of free add-ons for MT4 with a package they’ve called MT4 NextGen.

Features of Axi’s free MT4 NexGen:
- Sentiment Indicator
- Forex news
- Economic Calendar
- Session Map
- New terminal window
- Correlation trader
- Alarm manager
- Automated trade journal
- Mini Manager
Subscription Fees
Some of the larger forex brokers hire teams of foreign exchange market analysts and educators to help give their clients an edge. Check out some of the premium, subscription-based features below.
- Professional market research: Market research and analysis from some of the best economic minds in the business.
- Trader education: Alongside each forex broker’s public offering, private educational classes and webinars are available for an extra fee.
- Trading signals: If you’re not interested in learning to trade forex, subscribing to trading signals from a broker or partner may be what you’re looking for.
A lot of forex brokers offer premium, subscription-based features free for clients. You can also access a lot of interesting analyses and educational content with just a demo account. Always do your research between forex brokers before spending additional money on premium features or services.
Why Understand How Forex Brokers Make Money?
It would help if you understood how forex brokers make money so you can choose the right forex broker for you. While most forex brokers have a few standard charges that you’ll need to become familiar with, we dive a little deeper to help you fully understand the relationship between a forex trader and a forex broker.
To become a consistently profitable forex trader, you must understand where your money is going. We’re here to help you choose the best forex broker and trading account type for your own trading style.
The Importance Of Using A Regulated Forex Broker
Now that we’ve answered the question, “How do forex brokers make money?” and what each business model means, let’s shift gears to regulation.
Whether you trade with an ECN forex broker or a market maker, you should always ensure they’re regulated. Regulation should be a significant factor when choosing a forex broker, as you never know when you will need guidance.
Here are some forex broker regulatory factors to consider:
- Safety of your funds: Regulated forex brokers will not mix clients’ funds with business operational funds. This ensures that in the case of the broker going belly-up, your funds will always be safe.
- An avenue of recourse in case of any disputes: If you’re unhappy with your broker’s response about a trading issue and would like to escalate the problem, then having a regulatory body to turn to is vital. You never know when you’ll need assistance in the future.
- Transparency of operations: Regulated forex brokers must be fully transparent to regulators about the brokerage’s trading and business side. Regulation ensures transparency.
You can view our compare forex brokers homepage to compare the best UK brokers with FCA regulation.
Final Thoughts
When deciding whether to trade with an ECN forex broker or market maker, there is no correct answer.
There is no such thing as the right broker. No one type of broker is better than another, simply because of how they make their money. Each business model has pros and cons that appeal to different kinds of individual traders.
Would you rather trade on spreads as low as zero with commissions, or would it work out better for your trading if you just paid a commission-free spread markup?
Would you require fixed spreads that only a market maker can offer for your trading strategy?
These are questions that only you as an individual can answer!
In conclusion, it’s worth ending this article by saying that contrary to popular belief, no forex broker is your enemy. Go with whatever works for you and your trading style.



Ask an Expert