In this beginner’s guide, you will learn what interest rate trading is about and how to use it in your daily forex trading routine, etc. In the end, you should be able to implement some trading strategies into your forex trading account and optimize your trading approach.
What Is Interest Rate?
An interest rate is a cost or fee on a given amount of money that a borrower pays to a lender for a loan, typically quoted as a percentage of the principal.
Interest rates are set by the national central bank. These are the official interest rates that work in the country’s monetary policy, and all its elements (rate of inflation, stability of the financial system, etc).
A list of the most influential central banks around the world is as follows:
- U.S. Federal Reserve System (Fed)
- European Central Bank (ECB)
- Bank of England (BOE)
- Bank of Japan (BOJ)
- Swiss National Bank (SNB)
- Bank of Canada (BOC)
- Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA)
- People’s Bank of China
- Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ)

What Is Carry Trade Strategy?
Carry trade is the term for a strategy that allows you to earn passive income in forex trading by taking advantage of the interest rate differential between two currencies. Therefore, understanding how to trade interest rates using a carry trade is crucial.
Unlike other strategies that require market forecasting, the carry trade generates profit through daily interest payments, offering a more stable return. While no strategy guarantees success, this method can help you profit without predicting market direction.
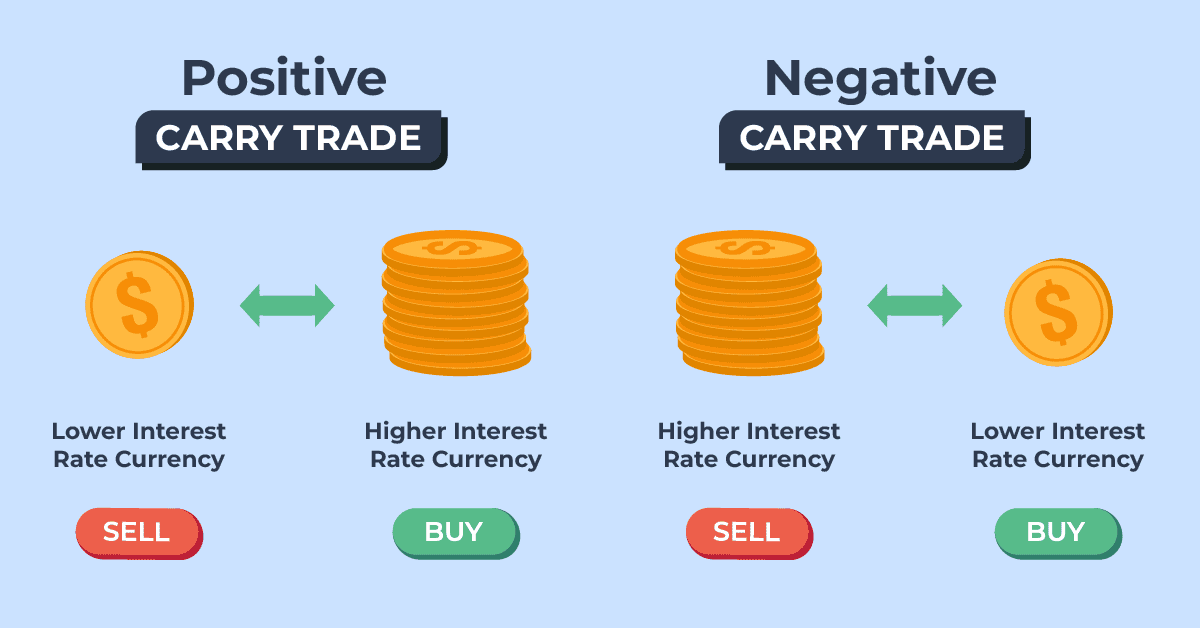
What Moves Interest Rate Markets?
Interest rate markets are influenced by a range of factors:
- Macroeconomic indicators: Higher or lower growth, inflation, consumer spending, Consumer Price Index (CPI), or employment numbers typically affect interest rates. Higher growth usually brings higher rates, while lower growth is often rewarded by the opposite.
- Central bank policy: Central bank’s interest rate decisions are based on their views of how the economy is performing in the economic calendar and their policy targets.
- Inflation Expectations: Inflation expectations have an impact on the currency market and where interest rates settle. Higher inflation expectations mean higher interest rates, while lower inflation expectations mean lower interest rates.
- Expectations: Expectations about future economic conditions often play a crucial role in interest rate markets too. So, for instance, if investors think that the US economy is about to slow down significantly, this should exert downward pressure on interest rates.
- Global shocks: The interest rate markets respond to developments on the international scale, such as geopolitical tensions, trade negotiations, or financial crises at the global level.
What Is Interest Rate Trading in Forex?
In the context of forex, the interest rate of a currency can influence its value. Higher interest rates typically attract investors seeking better returns, increasing demand for that currency, while lower interest rates might have the opposite effect.
Many brokers offer demo accounts where you can practice your interest rate trading strategies and learn how to trade interest rates in forex before investing real money.
How Interest Rates Move The Forex Market
The interest rates of central banks represent one of the forex market’s most direct drivers on the price action of the foreign currency pair. As a simple example:
- Rate hikes tend to increase a currency’s value.
- Rates down lead to the depreciation of the currency.
Therefore, when central banks announce changes in rates, whether to raise or lower them, it has a pronounced effect on foreign exchange market movements. A surprise change in rate from the central bank can produce large spikes of volatility in the forex market.
In effect, as the economy expands, interest rates will generally go up, and as the economy contracts, rates tend to fall to promote greater economic activity.
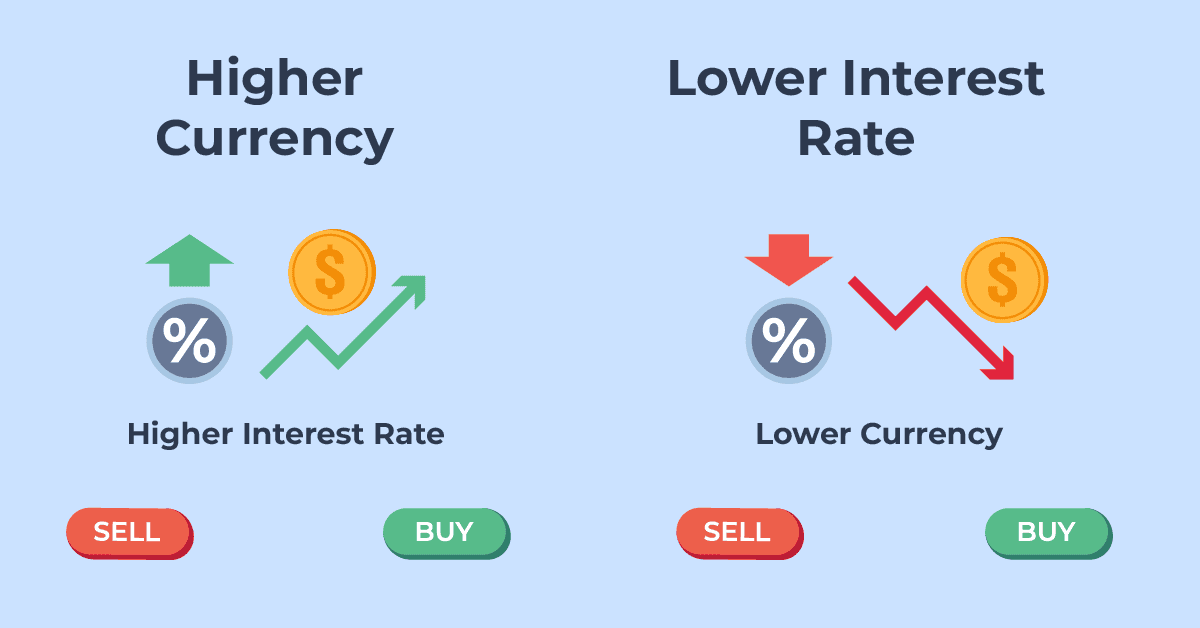
What Is An Interest Rate Differential?
The interest rate differential (IRD) is the difference in interest rate between two currencies. If the interest rate of currency A is 4.5% and the interest rate of currency B is 0.5%, the interest rate differential between currency A and currency B is 4.0%.
Note* High-yielding currencies tend to attract more capital and are more likely to rise over the long term.
The table below displays the current interest rates for 2025 across various countries.
This data is crucial for understanding global financial conditions and can impact investment decisions, currency exchange rates, and economic forecasts.
| Number of Country | Country | Central Bank | Interest Rate | National Currency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | The People's Republic of China (PBOC) | 3.35 % | Yuan (CNY) |
| 2 | United States | U.S. Federal Reserve System (Fed) | 5.50 % | US Dollar (USD) |
| 3 | Canada | The Bank of Canada (BOC) | 4.25% | Canadian Dollar (CAD) |
| 4 | New Zealand | Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) | 5.25 % | New Zealand Dollar (NZD) |
| 5 | Australia | Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) | 4.35% | Australian Dollar (AUD) |
| 6 | United Kingdom | Bank of England (BOE) | 5.00% | British Pound (GBP) |
| 7 | Euro Zone | European Central Bank (ECB) | 4.25% | Euro (EUR) |
| 8 | Japan | Bank of Japan (BOJ) | 0.25% | Japanese Yen (JPY) |
| 9 | Switzerland | Swiss National Bank (SNB) | 1.25% | Swiss Franc (CHF) |
Forex Interest Rate Trading Strategy
Carry trade is a forex trading strategy based on interest-rate differentials between currencies that involve exploiting the relationship between low and high short-term interest rates.
Basically means you borrow a currency with a low interest rate and invest in a currency with a higher interest rate. The profit comes from the interest rate differential between the two currencies.
This strategy is most effective in stable markets where exchange rates are not expected to fluctuate significantly. It allows traders to earn from the interest rate difference without relying on currency price movements.
Here’s a closer look at how to effectively implement this strategy:
Identify High Interest Rate Differentials
First, you have to go to currency pairs where there is a large interest rate differential.
For example, in the AUD/JPY if the Australian dollar has a higher interest rate than the Japanese yen, if you buy the pair AUD/JPY the return will be higher.
Choose the Right Forex Broker
Different brokers will offer different swap rates on different currency pairs. The percentage swap spreads can reduce your returns.
So make sure you pick a broker that offers good swap rates on the currency pairs you chose for your carry trade strategy.
Timing and Market Conditions
You need to manage your entry so that you enter the trade when an interest rate is expected to rise on one currency while it stays the same or declines on the other.
Also, low market volatility tends to be a plus – it means that the expected returns are likely to be higher.
Long-Term Holding and Risk Management
ince the typical carry trade holds a position over a long period to build up interest earnings, stop-loss orders are a useful way to guard against fast, adverse moves.
Analyze Economic and Technical Factors
You can complement your basic fundamental analysis of economic conditions – for example, monitoring inflation, GDP growth, and employment rates to anticipate interest rate changes – with technical analysis to improve the timing of your trades, and to identify when to get in or out.
Example Of A Carry Trade
If, as of Dec 2021, the national interest rate for the two currencies that make up the AUD/USD pair is as follows:
In the USA, the benchmark interest rate set by the FED is 0.25%
In Australia, the benchmark interest rate set by the RBA is 0.10%
The interest rate differential between the two currencies is 0.15%. A positive carry trade strategy would be to go short or to sell the AUD/USD FX pair. By going short AUD/USD, you’re basically selling Australian dollars and buying U.S. dollars.
The 0.15% will be paid out daily after the 5:00 PM rollover time in New York. The amount debited in the form of the rollover fee will also depend on how big your forex position would be.
The rollover formula is as follows:
Rollover = Position size * (Base currency interest rate – Quote currency interest rate)/365 x Exchange rate
The AUD/USD exchange rate as of 19 Dec 2021 is 0.7737.
Now if you open a short position with a standard lot of 100,000 units at 0.7737, you have the potential to gain USD 0.31 per day for the entire time the position is held open.
Rollover = USD 100,000 X (0.10% – 0.25%) / 365 X 0.7737 = USD -0.31
Although USD 0.31 seems like a small amount, when leverage is involved and the position is held open for the long term, over time it can provide a substantial interest income.
Pros and Cons of Carry Trading
Pros:
- Steady Income Stream: Carry trades provide daily interest payments from the interest rate differential, creating a consistent source of passive income over time.
- No Need for Market Forecasting: This strategy allows traders to earn without predicting price movements, as profits are driven by the interest rate difference.
- Potential for Long-Term Gains: In stable markets, carry trades can yield steady, long-term returns, allowing traders to hold positions for extended periods.
- Leverage Opportunities: Leverage enhances the size of your position, increasing potential profits from the interest rate differential, but must be used with caution.
Cons:
- Currency Risk: Exchange rate fluctuations can erode or even surpass interest gains, leading to capital losses if the higher-interest currency depreciates.
- Leverage Risk: While leverage can boost profits, it also magnifies potential losses, particularly when the market moves sharply against your position.
- Market Instability and Volatility: Sudden economic or political events can trigger volatile market conditions, resulting in unexpected losses for carry traders.
- Limited in Low-Interest Environments: When interest rates are low globally, the potential for significant returns diminishes, making carry trades less profitable.
My Final Thoughts
Currency carry trade is ideal for forex traders with a full-time job or career who seek an additional source of income.
Understanding how to trade interest rates in Forex can provide steady returns through interest rate differentials, but it’s not ideal for those needing frequent income.
For short-term traders, other strategies and instruments like CFDs offer more frequent opportunities.
The carry trade is one of the few strategies that rely on both technical and fundamental analysis. A detailed understanding of economic indicators, central bank policy direction, Forex Patterns, and market sentiment is therefore essential.
Risk Disclaimer
To profit from the carry trade, the interest earned must outweigh any potential losses from unfavorable exchange rate fluctuations.



Ask an Expert