Trading Forex
When compared to other financial markets like bonds or stocks, forex markets are the largest globally, turning over $6.6 trillion daily and valued at a staggering $2.409 in total. While many presume trading forex (foreign exchange) is only accessible to institutional investors, forex brokers and online trading platforms mean there are few barriers to entry for retail traders.
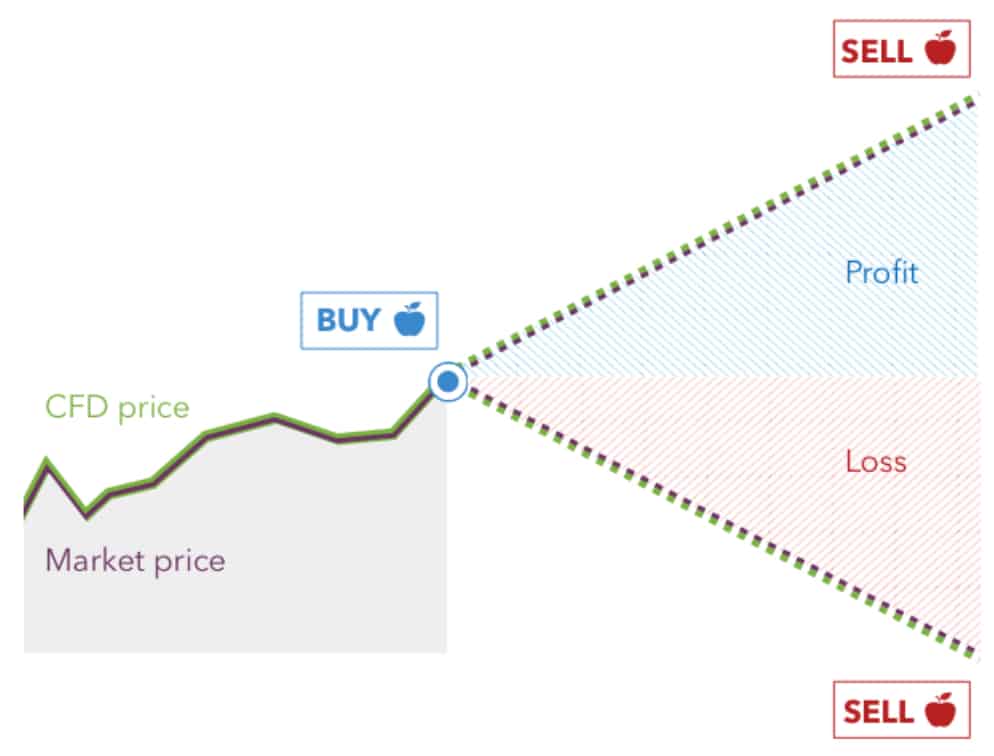
When fx trading, you simply exchange one currency for another at an agreed-upon price. When you start trading with an online broker rather than trading physical currency pairs, you will trade contracts for difference (CFDs).
CFD Trading
Contracts for difference (CFDs) are a type of derivative product that allows you to speculate on an instrument’s price movements, without actually buying or selling the physical underlying asset. A major benefit when trading CFDs compared to the underlying physical asset is that you can use Leverage, magnifying your exposure beyond your initial investment.
CFD Asset Classes
While different brokers offer different CFD product ranges, most top forex brokers will provide access to a combination of the following asset classes:
- Forex: Forex markets consist of 170 different currencies, with major, minor, and exotic fx pairs (i.e. GBPUSD) available to trade as CFDs. Commonly traded currencies include the US Dollar (USD), Great British Pound (GBP), Japanese Yen (JPY), and Swiss Franc (CHF).
- Indices: Major equity markets such as the ASX 200 Index, UK 100 Index, and the US SPX 500 Index.
- Commodities: Many types of commodities can be traded as CFDs, i.e. precious metals, energies, oil and gas, and agriculture products.
- Stocks: Shares across major stock exchanges like the NYSE, ASX, and NASDAQ are offered by certain brokers. Stock markets are only accessible via certain trading platforms like MetaTrader 5.
- Bonds: Bond instruments issued by governments such as the United States, United Kingdom, Germany, Switzerland, and Japan.
- Cryptocurrencies: Online brokers may offer CFDs for cryptos like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Dash amongst other major and emerging cryptocurrencies.
- Other CFDs such as Futures, interest rates, ETFs, options, mutual funds, and hedge funds may also be available with some forex brokers.

Choosing a Forex Broker in Australia
As an Australian trader looking for a forex broker, there are key factors to consider and understand. There are hundreds of broker and trading platform options that suit different styles of trading and levels of experience, therefore it is vital to know what CFDs and trading tools you require, along with the trading strategies you plan to execute. Key considerations should include:
- The type of broker – no dealing desk vs dealing desk brokers.
- Your preferred trading account type and pricing structure – standard accounts with no commission vs ECN accounts with commission fees.
- The trading platform and tools you want access to.
- Investor protection is required, as well as risk management tools and ASIC regulation.
Types of Forex Brokers
Forex brokers fall into one of two major categories – dealing desk brokers (known as Market Maker) or no dealing desk (NDD) brokers. Different pricing and commission fee structures are available with the two types of brokers, meaning it is important to know how your broker is executing orders.
1. Dealing Desk Brokers
Via a dealing desk, market makers use their own internal liquidity to fill your orders while setting their own bid-ask prices. As discussed further in the next section, market maker brokers offer commission-free forex trading. Rather than paying an additional commission fee on top of the spread, market makers widen their spreads to compensate for their brokerage services. Some forex traders believe market makers lack transparency, as they are the counterparty to your trades and therefore profit off your losses.
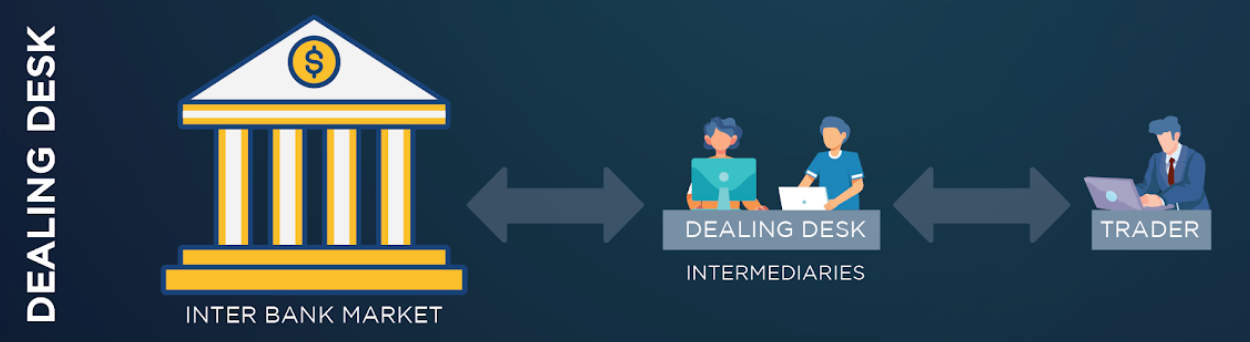
2. No Dealing Desk Brokers
NDD brokers use either straight-through processing (STP) or electronic communications network (ECN) technology to execute orders, with some brokers using a combination of the two. With no dealing desk interference, NDD brokers pass your orders directly onto external liquidity providers that fill your order and are the counterparty to your trade. As multiple top-tier liquidity sources are utilised, NDD brokers can offer ultra-tight spreads and fast execution on par with an institutional-grade trading environment.

The key distinction between ECN and STP brokers is the control the broker has over the external liquidity sources. ECN brokers have no control over the liquidity providers they use, while STP brokers retain some control.

3. Dealing Desk vs NDD Brokers
The two types of brokers suit different trading experience levels and strategies. If you are a beginner trader wanting a simple fee structure, market makers offer a soft entry into forex trading. Yet, if you are an experienced trader wanting to execute day trading, scalping, or algorithmic trading strategies, NDD brokers offer tighter spreads and faster execution speeds.
Trading Account Types and Spreads
Depending on whether your broker is a market maker or an NDD broker, you will have the option of two main pricing structures when trading forex.
- NDD Brokers – Offer commission accounts where you pay the forex spread + a round turn commission fee.
- Market Makers and NDD Brokers – Offer commission-free accounts where you pay the forex spread + no commission fees.
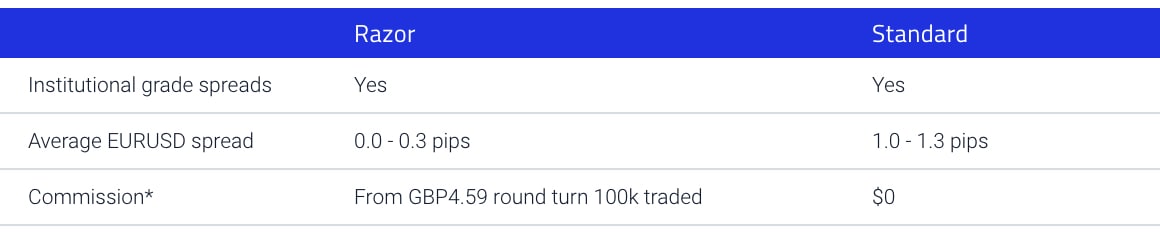
For example, Pepperstone offers two account types, a Razor account with commission spreads and a Standard account with no commission fees. IC Markets is similar.
To see potential gains or losses from trades, you can use our forex profit calculator.
Your Profit
Profit in pips:
Profit in Pips Calculation
= ( Close Price - Open Price ) / 0.0001 x Trade size
= ( - ) / 0.0001 x
Profit in Pips Calculation
= ( Open Price - Close Price ) / 0.0001 x Trade size in lot
= ( - ) / 0.0001 x
Profit/Loss Calculation:
Profit/Loss in Calculation
= Profit in Pips x Pip value
=
Commission Account Types
Often referred to as ECN accounts, commission trading allows you to access ultra-tight spreads that can be as low as 0.0 pips thanks to NDD execution. As you are trading spreads sourced directly from external liquidity providers, for each trade you pay a round-turn commission fee for each 100k traded.
As NDD brokers use different liquidity providers, average spreads vary. As shown below, brokers like Pepperstone and IC Markets provide access to the tightest ECN spreads. Overall, IC Markets offer the lowest average spreads for the major currency pairs shown below, such as the EUR/USD (Euro vs US Dollar) and the AUD/USD (Australian Dollar vs US Dollar).
Avg. spreads are taken from each broker's website and updated monthly. Last update on 07/01/2025
Commission-Free Account Types
Commonly called classic or standard accounts, commission-free account types are ideal for beginner traders wanting a simple pricing structure. Both NDD and market maker brokers offer this account type where you pay no additional commission fees on top of the spread.
While ECN spreads can be as low as 0.0 pips + commission, spreads with no commission fees mostly start from 1.0 pip. As shown below, IC Markets provides access to the tightest spreads for most Major Forex Pairs, averaging 1.40 pips for the GBP/USD and 1.10 pips for the EUR/USD.
Avg. spreads are taken from each broker's website and updated monthly. Last update on 07/01/2025
As well as the two main pricing structures and account types, brokers may offer the following account options:
- Islamic Accounts: Also known as swap-free accounts, Islamic accounts are designed for forex traders following Sharia Law that cannot make or receive payments derived from interest rates.
- Micro Accounts: This allows you to trade smaller lot sizes known as micro-lots. Accounts with smaller trading volumes available usually require smaller initial minimum deposits.
- VIP Accounts: Often reserved for those trading higher volumes or making larger deposits into their trading accounts.
- Professional Accounts: For those with past experience in the industry wanting to trade high volumes of fx.
Forex Trading Platforms
While there are many trading platforms available, most retail forex traders will use one of three, being MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, and cTrader. The mainstream platforms are offered by various brokers and provide a range of trading tools to enhance your strategies. Alternatively, certain brokers offer proprietary trading platforms, as well as additional mainstream options.
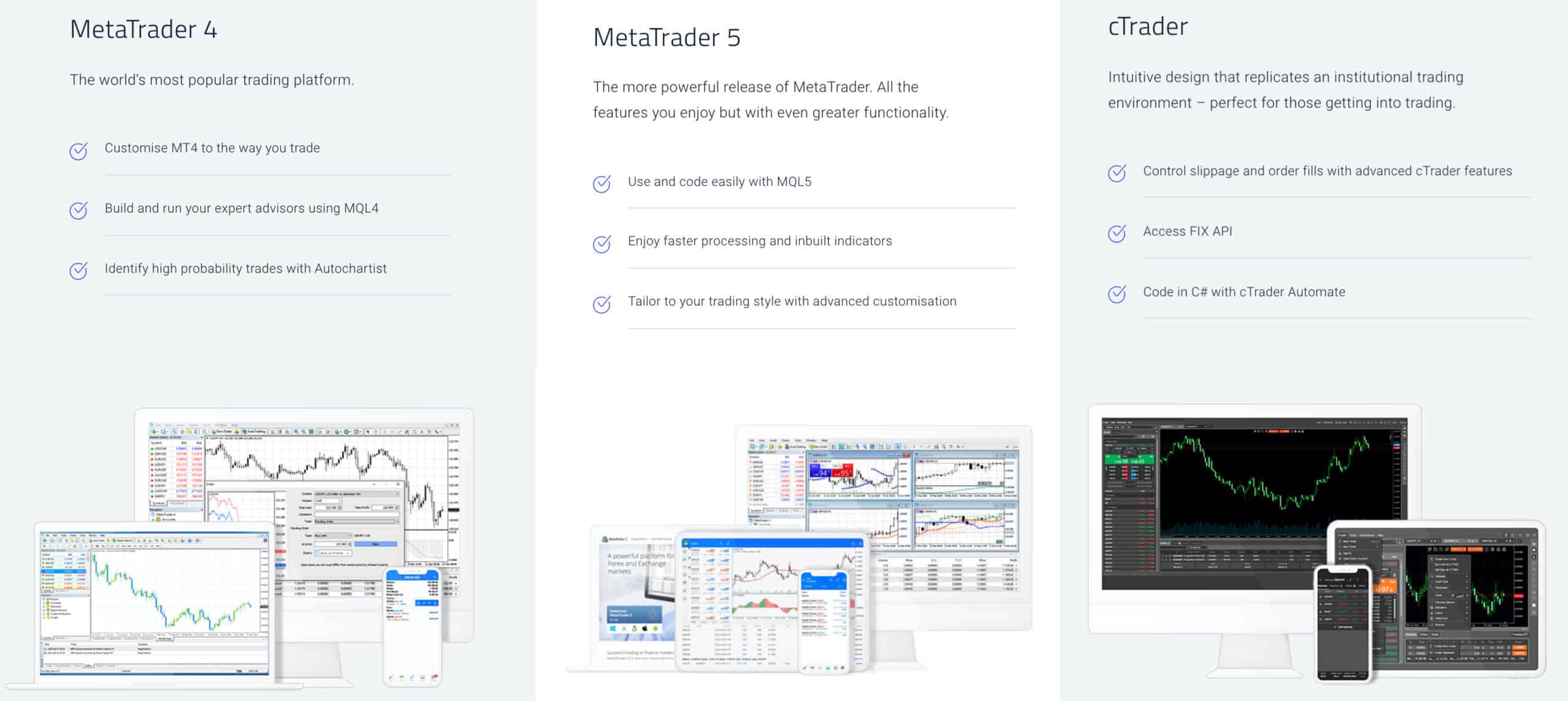
Mainstream Platforms
MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), and cTrader are the three most popular trading platforms globally thanks to being the most advanced Automated Trading Platforms. You can achieve full automation using algorithmic features, known as Expert Advisors on MT4 and MT5 and cBots on cTrader. You can either write your own trading robots or download tried and tested EAs and cBots online. Other features include:
- Advanced technical analysis tools with inbuilt charting packages.
- Backtesting features to test and optimise cBots and Expert Advisors (EAs).
- Proprietary programming languages with MQL4 (MT4), MQL5 (MT5) and C# (cTrader).
- Trades can be executed on either desktop trading platforms, web trader platforms, or mobile apps for Android and iOS devices.
- Suited to scalping, day trading, and hedging.
- Third-party social-copy trading features that can be integrated into the platforms are offered by some brokers.
Proprietary Platforms
There are numerous brokers that offer proprietary platforms unavailable elsewhere. While these platforms may offer trading tools well-suited to those new to trading forex, most lack the advanced technical analysis and algorithmic features that MT4, MT5, and cTrader provide. Examples of brokers with popular proprietary trading platforms include:
Plus500: As a market maker, the broker’s proprietary platform offers premium risk management features such as guaranteed stop-loss orders.
eToro: A social-copy trading network and platform that allows you to automate trading through account mirroring features. You can copy the trading strategies of other forex traders as well as interact and learn from them. The eToro platform make use of AI technology to help you find the best signal providers for you to follow.
Forex Markets Regulation and Risk
As foreign exchange markets experience significant volatility combined with the leverage available to retail traders, trading forex comes with a high risk of losing money. The rules and regulations surrounding forex trading vary between countries, with brokers offering different risk management tools to assist traders.
While in some countries the local regulator also acts as the Central Bank (i.e. Singapore), Australia’s financial authority operates as a separate supervisory agency that provides independent advice regarding forex trading rules in Australia.
ASIC and Australian Regulation
Aussie brokers are overseen by the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) and must hold an Australian Financial Services License (AFSL) to operate in Australia. Since 2022, ASIC’s forex trading regulations follow the standard in the UK (FCA) and Europe (ESMA). This is mainly due to the high risk that comes with trading leveraged products and with the aim of reducing the number of distressing financial situations caused by losing money when forex and CFD trading.

In addition to basic investor protection policies such as segregated client funds, product disclosure statements (PDS), and website disclaimers, ASIC protects traders from large losses by requiring brokers to offer the following:
- Negative balance protection and close-out margins.
- Leverage caps reduce forex leverage from 500:1 to 30:1.
- Restricted promotions such as rewards and gifts.
Risk Management Tools
To help you reduce the high risk that comes with forex trading, brokers provide risk management tools such as demo accounts and order types.
Project management tools can also help by allowing you to track all your trading accounts (if you have more than one).
Demo Accounts
Demo accounts allow you to practice trading in real-time market conditions, in a risk-free environment. With virtual account balances, you can place orders in foreign exchange markets, allowing you to test out trading strategies, new Expert Advisers, and much more.
Order Types
To protect yourself against large fluctuations that are common with exchange rates, different order types can be used to maximise profits while minimising losses. Most brokers offer basic order types like stop losses, trailing stops, and limit orders, while premium orders such as guaranteed Stop Loss Orders (GSLO) are only available via market maker brokers.
How to Trade Forex – An Example
Assume a trader believes that the value of the AUD will appreciate or rise against the value of the YEN. An alternative way of thinking about this situation is that the YEN will devalue in relation to the AUD.
They buy the AUD/YEN at 1.1500 and purchase $6,000 worth of currency. Later that day, the price increased to 1.1550. The trader is up $30 (6000 * 0.0050). If the price dropped to 1.1430, the trader would be losing $42 (6000 * 0.0070).
Due to the fact that currency markets trading hours are on the go twenty-four hours a day, experienced traders may choose to hold their position in a currency pair overnight. Their chosen broker will allow for the rolling over of their position, with the individual ultimately receiving either a debit or a credit, determined by the interest rate differential between the AUD and YEN. If the interest rate of the AUD is higher, post roll over the trader will receive a credit, however, if the opposite was to be true, and the interest rate of the YEN is higher, the trader would receive a debit.
Use our Time Zone Converter to determine the best trading hours for you.
The concept of rollover can determine the outcome of any trading decision. This is specifically true when traders have the intention to hold positions for the long term. The other point of strong consideration is the varying differences in interest rates. If there are large variances, this can result in significant credits or debits on a daily basis. If chartered incorrectly, this can erode the generation of profits or even worse, increase losses on a specific trade.
As mentioned above, a forex example would be incomplete without a consideration of major forex risk being leveraged. Currently, brokers in Australia can provide leverage with a range varying up to 500:1. In this example, let us assume that the trader used the leverage of 50:1. If using 50:1 leverage, although the value of their trade will be worth $5,000, this is not the amount of money they will be required to invest. They will only need a substantially more minute amount of $100. As long as the trader has $100 and 50:1 leverage, they will be able to trade with $5,000 worth of currency.
Making a profit of $30 off one trade whilst knowing that the trader only needs $100 (this can be even less if more leverage is deployed) accurately displays both the power and the downside of leverage. However, if a trader does not acknowledge the risks involved when it comes to leveraging, the capital in their account will dwindle quickly. A list of Forex Courses can help further explain the concept of forex.
What Factors Affect Market Prices?
When trading forex and CFDs, it is important to be aware of the various factors that affect an asset’s price, such as changes to economic conditions or inflation. If you are new to trading and unsure of the significant macroeconomic factors to follow when trading, brokers like Pepperstone offer excellent educational resources.

For example, the video below explains 5 key macro fundamentals to consider when trading forex and CFDs:
- Politics
- Inflation vs deflation
- Central Banks and Monetary Policy
- Growth
- The relative attractiveness of a country
Forex Trading Patterns
Forex trading patterns are recurring chart formations traders use to predict price direction. As a trader, technical analysis is your primary tool to use before opening any new position. Let’s break down how to leverage candlestick and harmonic patterns to sharpen your strategy.
Candlestick Patterns
Candlestick patterns visualize price action within a given timeframe, signalling when momentum shifts. Red candles represent sellers, and green candles represent buyers. Over time recurring forex candlestick patterns occur and your goal is to use them to measure momentum and market sentiment.
Here are the primary types of forex candlestick patterns.
Bullish Candlestick Patterns
Bullish candlestick patterns (e.g., double bottom) signal potential price rises for buy setups. These patterns signal that sellers are exhausted, and that buyers are stepping in, driving prices higher.
For example, when a hammer candlestick forms after a downtrend or a bullish engulfing candle swallows prior losses, it’s a sign of shifting momentum. When key support areas get tested successfully, or traders spot bullish patterns, this leads to a chain of long positions.
Bullish Candlestick Patterns
Bearish candlestick patterns (e.g., shooting star, evening star) warn of pending price declines and sell opportunities. When prior buyers close their longs, you will see certain clues in the chart, such as a head and shoulders or evening star pattern.
These bearish forex patterns represent late long positions getting liquidated, often leading to sudden drops as sell orders fill the market.
As a trader, one of the best approaches is to combine candlesticks with key levels (like daily highs/lows) for higher probability trades.
Advanced Patterns
Advanced Candlestick Patterns (e.g., harmonic structures) combine multiple candles and Fibonacci ratios for precise entries/exits.
Harmonic patterns (my secret weapon) turn Fibonacci ratios into actionable setups. These patterns leverage the naturally occurring mathematical fractals to give you long and short setups as well as targets to take profit.
Reviews of Top Brokers
Brokers offer different functionality, latency, and charting that are critical to trading with margin and the overall trading experience. The forex broker selected will set the trading platform options available, the financial market, and features.
Pepperstone
Pepperstone is a Melbourne-based ECN forex broker allowing trading directly with liquidity pools. Their main features include:
- The choice of MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), or cTrader.
- Industry-leading leverage of 30:1.
- Fast execution speed with the use of Equinix servers in New York and London.
- Award-winning (Investment Trends) customer service.
- UK Spread betting facility for UK traders.
- Buy and sell cryptocurrencies, index CFDs, futures, and commodities.
- Easy account management with fee-free deposits and withdrawals in your account base currency.
Pepperstone offers the most popular forex trading platforms, low spreads and commissions, High Leverage Forex Brokers, and execution speeds are why they are recommended for intermediate to expert forex traders. You can compare Pepperstone to other ASIC-regulated firms on the Best Australian Forex Broker List.
Pepperstone ReviewVisit Pepperstone
Go Markets
GO Markets is a Sydney-based forex broker with a tiered service approach.
The brokers’ core features are:
- The offering of MetaTrader 4 Genesis with enhanced features and charting.
- Low spreads and fees depend on the deposit made within the account.
- Extra financial services include buying and selling binary options.
- 30:1 leverage
- VPS option to speed up the forex trading environment.
GO Markets is an excellent option but only for those that opt for their new GO Markets PLUS account. This account has the lowest fees with raw spreads and Australia Dollar $3.00 per side commission. The issue is that regularly the minimum deposit is $10,000 making this broker only suitable for high-volume currency traders. If you’re a high-frequency trader, then you should consider this forex broker.
GO Markets ReviewVisit GO Markets
easyMarkets
easyMarkets is a Cyprus-based forex broker regulated by ASIC as well as other financial authorities around the world.
Their main strengths are:
- Deal Cancellation allows forex trades to be canceled within 60 minutes.
- Risk management safeguards include guaranteed stops and Negative Balance Protection for all traders regardless of location.
- Fixed spreads and no commissions, providing transparent trading costs.
- 300+ financial markets, including the option to buy and sell cryptocurrencies.
- 400:1 leverage when trading foreign exchange.
easyMarkets offering of transparent trading fees, combined with unique risk management tools, make them the ideal forex broker for beginner forex traders with a low-risk profile. They focus on those new to trading but are not the best in the category as you can view on the forex broker beginner page.
easyMarkets ReviewVisit easyMarkets
Plus500
Plus500 is a publicly listed company that has an office in Sydney.
The forex broker offers to trade with:
- 300:1 leverage.
- The broker’s proprietary forex trading platform.
- No commission trading with variable spreads.
- Share trading of the ASX 200 and other financial services.
- Risk management tools include guaranteed stops.
Plus500’s key strength is their offering of financial products outside of forex such as shares, though fees for all asset classes are high. If the brokerage is important to you, then view the Lowest Spread Forex Brokers comparison page.
Their CFD trading platform is unique to the other Australian forex brokers, which are both their strengths and weakness if you want to change brokers at a later stage.
*Your capital is at risk ‘72% of retail CFD accounts lose money’
For more information, you can read full reviews of popular ASIC-regulated brokers: Markets.com Review, IC Markets Review and ThinkMarkets Review.


















Ask an Expert
What is cheaper, ECN, STP or Market Maker?
While all 3 are excellent options and there are a few subtle differences they are mostly just marketing terms. All 3 offer excellent spreads however ECN and STP tend to offer better spreads than Market Makers
Do I have to report forex income?
Depend on what country you are in but most likely you will need to report any capital gains taxes.