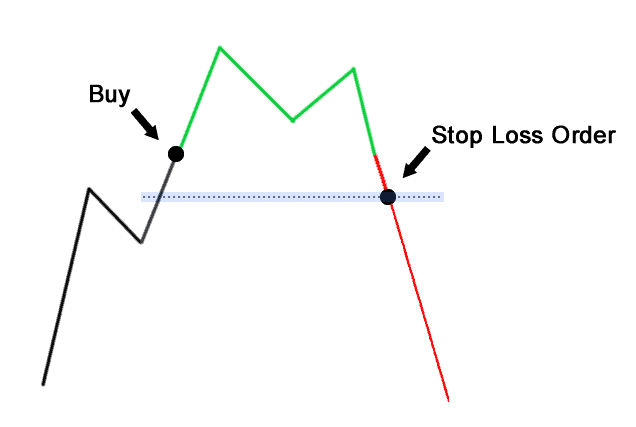
What Is Stop Loss In Forex?
A stop-loss order when forex trading is a risk management tool that instructs your broker to automatically exit your open trading positions when the price drops to an undesirable level. Learn more about stop loss in our guide.
Written by Justin Grossbard
Updated:
- 67 Forex Brokers reviewed by our expert team
- 50+ years combined forex trading experience
- 14,000+ hours comparing brokers fee + features
- Structured and in-depth evaluation framework
Our broker reviews are reader supported and we may receive payment when you click on a partner site.
There are several types of orders that involve a stop loss.
1. Stop Loss Market Orders
With a stop loss market order, your broker will automatically close the position when the current market price nears your set limit. The key to note is that the trade is closed at the current market price. This means that the exit price will usually be close to your set limit, but is still susceptible to slippage during high-volatility market conditions.
2. Stop Loss Limit Orders
Rather than fulfilling the order at the next available price, a stop loss limit order will instruct your broker to automatically exit the trade at a specified limit. If the set stop loss price is reached, the limit order will be automated and the position will be closed at the stop-loss price or better. This difference helps to avoid slippage.
3. Guaranteed Stop Loss
Some forex brokers offer what is called a guaranteed stop loss order. This feature is the same as a stop-loss, however, the broker guarantees that they will exit your trade at your set limit. While a regular stop-loss means the broker will ‘try’ to exit your position at your preferred price, they may not be able to do so due to slippage or low liquidity. With a guaranteed stop loss, your broker will pay you any differences between your stop loss price and the price they do exit you at if below your limit.
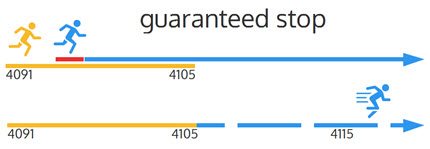
The peace of mind associated with a guaranteed stop-loss often comes with a small price. Most brokers will charge a small fee based on the size of your trade position due to the difficulty of liquidating such assets quickly. In other words, the broker may not actually be able to sell at the specified price, meaning they charge a premium for the guaranteed stop-loss.
4. Trailing Stop
A trailing stop is a type of stop loss order that automatically moves according to the fluctuating price. As mentioned previously, you can move the stop-loss price limit towards the current price, if your trade is profitable. This allows you to essentially follow the price and continuously place your stop loss further and further into profit. A trailing stop works in the same way as a regular stop-loss order, however, it is attached to the fluctuating price, allowing you to lock in profits.
5. Take Profit
A take profit order works in a similar way to a stop loss. However, a take profit order is fulfilled when a trade is automatically closed with a profit at a specified level, rather than a loss. When you place a trade, you may use a take-profit order to specify a price at which your broker will automatically close the position at a profit target. The take profit feature offers all the same benefits and drawbacks as a stop loss but works on the other end of the scale.
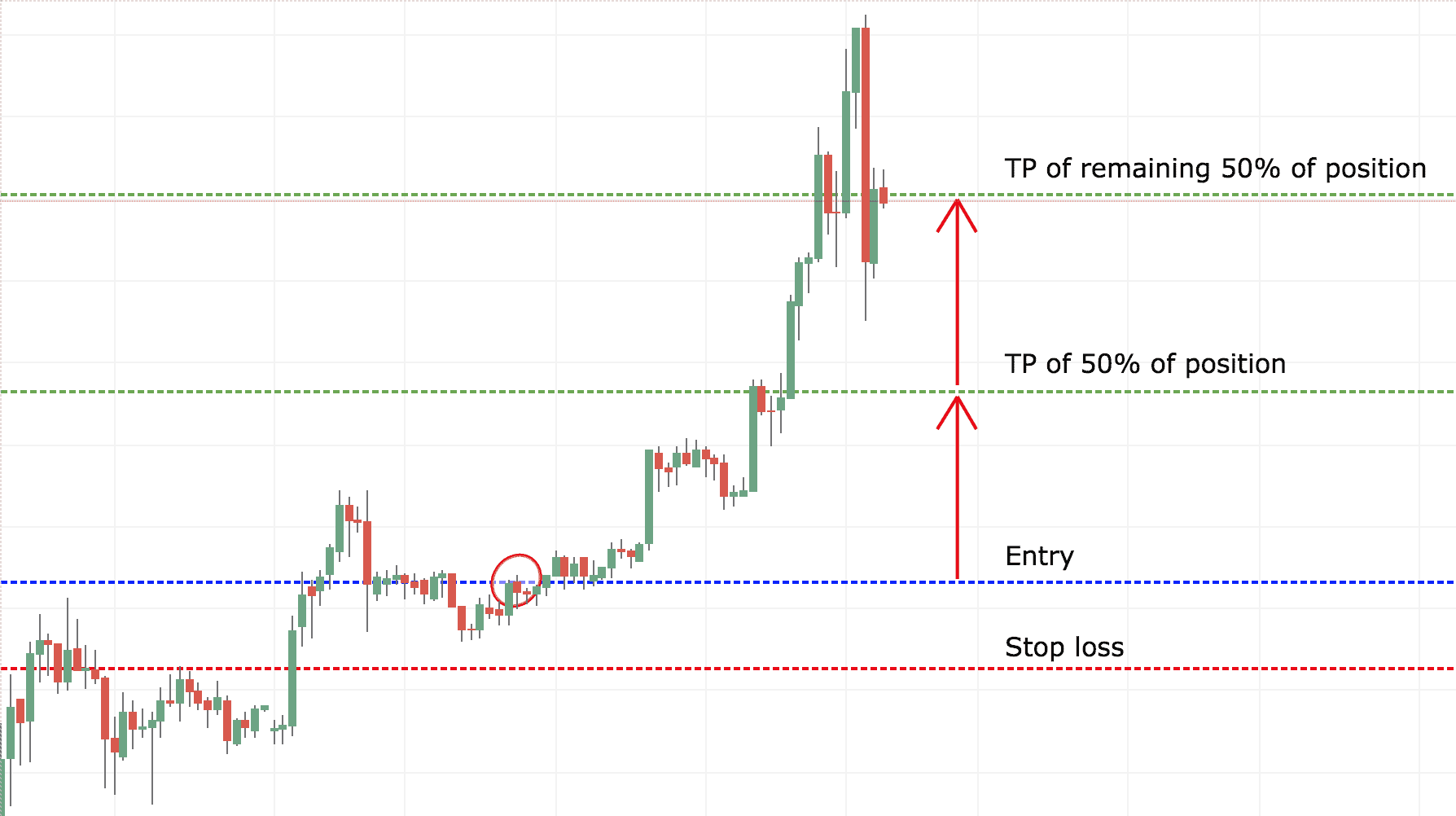
As an efficient and effective way to manage open trading positions, traders tend to use take profit and stop-loss in conjunction.
6. Guaranteed Take Profit
A take profit order is susceptible to slippage, however, a guaranteed take profit order is a tool that ensures the position is closed. This reassurance comes with a premium fee, as your broker may not always be able to close the trade. Using a guaranteed take profit, you are protected from any price discrepancies, and your trade will take profit as you specify.
7. Market Order
A Market Order is executed as an instant buy or sell order at the best available price in the market. For market orders, your broker will provide you with the best price they can offer on your trade against the market. As mentioned above, when using a Market Order, factors such as price discrepancies and slippage need to be considered as high volatility markets can mean that the order may not be fulfilled at the exactly specified stop-loss or take-profit price level.
8. Limit Order
A limit order is placed not at the current market price, but rather at a specified level above or below. Typically, traders place a limit order to buy below the market or sell above the market at a certain price. The trade is executed once the price hits the specified level, otherwise known as the limit price. Limit orders differ from other types as the order is triggered when the price becomes more favourable to you than the current price.
8. Pending Order
A pending order is not activated instantly, but rather it is executed in a specific time frame at a certain price. When you place a pending order, the trade will open when the price reaches the level you specified. Rather than waiting for the price to reach a certain level, you can place a pending order and the trade will be executed when the price moves and market conditions meet your specifications.
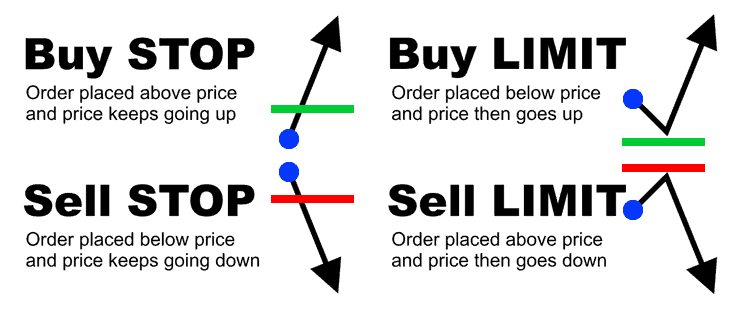
Stop Loss In Action
A stop-loss help protect your trade from excessive losses. The best way to demonstrate this is with an example:
Let’s say we have two forex traders who trade a range of currency pairs such as EUR/USD, GBP/JPY, AUD/USD, and CAD/USD.
- Trader 1 who sets their stop-loss size at 10% of their total account balance and
- Trader 2 who sets their stop-loss size at 1% of their account balance.
This means trader 1 has a more conservative risk management strategy, as they have instructed their broker to exit their trades earlier with their stop loss. If we assume:
- both traders have the same amount of funds in their trading account, and
- the same trading strategy,
then we can surmise that if both trader’s currency pairs move unfavourably and they lose 10 trades in a row, then trader 1 will be down 20%, while trader 2 trading account funds will be exhausted. With this scenario, we can surmise that it pays to set a higher stop loss level.

Pros And Cons Of A Stop Loss Order
Making this type of order is not as straightforward as it may appear.
1. Pros
Keeping in mind that a stop-loss is an automatic instruction to your broker to sell when the price reaches a pre-determined level, a stop loss presents a number of useful benefits.
- A stop loss removes human emotion, which can often interfere with logical day trading decisions. Setting a stop loss order means the influence of emotion is no longer a fact and forces you to stick to your trading strategy.
- Specifying a price level to exit a trade removes the need to constantly monitor your trades in person. Forex markets are operating 24 hours a day, so it is not possible to monitor the market at all times. Therefore, it provides an element of protection for when you are unable to trade.
- Forex trading inevitably involves wins and losses. Setting a stop-loss order mitigates risk and enables you to manage your trading funds and reduce drastic losses. This is even more important to consider when using leverage.
2. Cons
Although useful, stop-loss orders do have some drawbacks:
- A stop loss order does not guarantee you against future price rises – For example, setting a stop-loss order may cause the trade to close too early, meaning you will lose the trade despite making a defensive trading decision. In other words, the price may reach the stop-loss level, triggering a sell before reversing into a profitable position.
- Your stop loss order may fall victim to slippage – Liquidity in the forex market is constantly and rapidly changing and this results in lag time before the latest prices reach you and you can execute your trades. The price you set for the stop loss order may be slightly different from the price your broker is able to exit you at which may result in slight unexpected losses.
- Your broker may not be able to exit your position – In extreme economic events or when there is low liquidity in the market, it is possible that your broker may simply be unable to close your position if they cannot find a buyer. This can lead to significant losses for your trade. Fortunately, there are some strategies available to help reduce the chances of this happening such as call margins, margin limits, and guaranteed stop loss.
A Quick Note On Leverage
As changes in the forex market can be small, traders use what is called Leverage to enhance their positions and magnify their trading results. Leverage (sometimes called Forex Margin Trading) is a way to borrow more money to trade with. By accessing more funds, you can amplify your trading size and thus take advantage of the small price movements. For example, a trading account with $1,000 can use the leverage of 1:100 and therefore trade with $100,000 worth of capital. This sounds appealing, however, accentuating your trading results is both rewarding and risky.
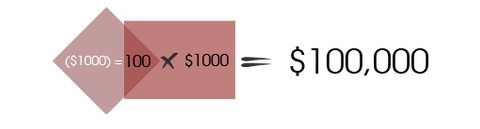
Borrowing funds to trade is risky. Using a stop-loss is a safer way to trade on leverage (or trade on margin) as it provides a level of protection against amplifying losses of capital you cannot afford to lose.
Limited Risk Accounts
Some brokers offer what is referred to as a Limited Risk Account, predominantly designed for beginner traders but also available to anyone. Brokers want to ensure that their clients’ trading accounts do not deplete and that their clients have a good experience trading with the chosen broker. For this reason, a Limited Risk Account is available to restrict excessive losses.
How Does A Limited Risk Account Work?
A Limited Risk Account works by only allowing traders to enter a position once a Guaranteed Stop Loss has been placed on the trade. You cannot trade unless a guaranteed stop-loss order is attached. Therefore, you cannot lose more than your trading account balance allows you to due to the predetermined maximum loss.
Trading Strategies Involving A Stop Loss
The stop-loss order is a convenient tool that allows you to reduce trading risk and potentially spend less time looking at the screen. Some trading strategies are available when using a stop-loss strategy.

Trailing Stop Loss
The trailing stop has already been mentioned and discussed, however, it is an extremely useful strategy for traders of all levels of experience. As far as downside protection strategies go, the trailing stop is extremely effective. It is an enhancement on the regular stop-loss because rather than using a fixed limit price, the trailing stop will follow a winning trade further into profit, meaning you can lock in profits along the way (assuming you’ve hit a winning trade). It is important to check the fees associated with your broker because trailing stops typically cost a premium to implement.
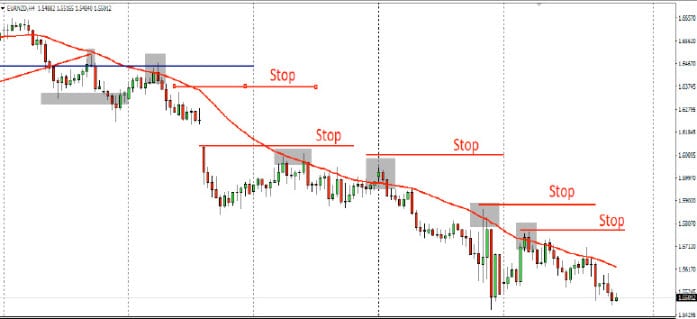
Chart-Based Stop Loss
A stop-loss order can be executed using trading charts. This is known as a chart-based stop, and it works off various market signals, indicators, and patterns within forex charts. This kind of strategy is better suited to traders with more experience in charting analysis and knowledge, as it relies on features such as trend line positioning, resistance levels, and support levels.
Percentage-Based Stop Loss
The most popular type of stop-loss order is the percentage-based stop-loss, which utilises predetermined proportions of your position size to calculate the limit value. Using a percentage-based stop-loss means you are only risking a certain percentage of your trading account when you set the order. The percentage may depend on factors such as risk appetite, confidence in the trade, or level of trading experience. It is important to note that this type of stop-loss order doesn’t factor in market conditions, but rather it is only based on the numerical amount you are willing to risk on a trade or your risk-reward ratio.
Volatility Stop Loss
Due to the volatile nature of the forex market, you can use a volatility stop to protect against price action fluctuations. A volatility stop is applied based on market volatility, rather than market value. During high-volatility market conditions, setting a wider limit allows you to take advantage of market swings. During low- volatility market conditions, the limits would be set narrower to the entry price in order to stay close to the target price level.
Final Words On Stop Loss
The volatile nature of the forex market makes stop-loss effective in protecting your trading account funds. With practice, setting a stop-loss correctly is a useful trading strategy to provide a safety net for losing trades. As always, it is recommended to test your skills and learn the process using a demo account before jumping into a live account. The feature may also be used to secure profits when price movement is in your favour. Whether you are a beginner forex trader or an experienced professional, stop-loss is a valuable trading tool for trading forex and CFDs. Many traders liken the stop-loss to an insurance policy – we hope to never need it, but it sure is wise to have the protection available just in case!
Justin Grossbard
Having traded since 1998, Justin is the CEO and co-founded CompareForexBrokers in 2014. Justin has published over 100 finance articles from Forbes, Kiplinger to Finance Magnates. He has a master’s degree in commerce and has an active role in the fintech community. He has also published a book in 2023 on investing and trading.



Ask an Expert
Which brokers provide guaranteed take profits and allow the straddle strategy
Brokers with a Guaranteed Stop Loss Order (which will also work for take profit) include CMC Markets, IG Trading, easyMarkets, Plus500, City index and OANDA. To use their GSLO, you need to be using the brokers proprietary platform.