What Is Margin In Forex
Margin trading when forex trading is a way to access borrowed capital provided you deposit enough funds to meet the lender’s margin requirements. Use of margin unlocks access to leverage so you can take larger positions with less of your own funds.
Written by Justin Grossbard
Updated:
- 67 Forex Brokers reviewed by our expert team (See our top 10 picks)
- 50+ years combined forex trading experience
- 14,000+ hours comparing brokers in the past 12 months
- Structured and in-depth evaluation framework (Our Methodology)
Our broker reviews are reader supported and we may receive payment when you click on a partner site. For more information, visit our About Us page.
Margin Trading In Forex
Margin trading allows you to speculate on financial markets such as cryptocurrency, metals such as gold and silver, and forex markets with just a small deposit. Margin trading is a tool used by traders to access leverage, which allows you to access more capital for investment or trading purposes than you may have at hand.
This article looks at what margin trading is and looks at some of the key concepts one should be familiar with.
What is Margin Trading
In forex and CFD trading, brokers allow you to trade on Leverage, provided you have the minimum amount of unused account balance he requires to open your position. This is known as margin trading. When trading with margin, your ability to open trades is not based on how much capital you have in your account, but on how much margin you have. Your broker needs to be assured you have enough cash to ‘set aside’ or use as a deposit before they will give you leverage.
Margin trading is the practice of using collateral to access leverage for investment purposes
When trading on margin, you can get greater market exposure by committing upfront just a small amount of money toward the full value of your trade.
What Is Margin?
In Forex trading, the margin is the amount you need to deposit or have in your account to access leverage or maintain a leveraged position. This deposit is a portion of the value of the trade or investment that you must ‘set aside’ or ‘lock up’ in your trading account before you can open each position you trade. Forex margin is not a fee or cost.
Margin is the amount of unused funds you need in your trading account to open and maintain your position
This deposit is a good faith deposit or form of security to ensure both the buyer and seller will meet obligations. It is not a down payment as you are not dealing with borrowed money in the traditional sense. When trading with forex and CFDs, nothing is actually bought or sold as you are dealing with agreements or CFDs, not physical financial instruments.
The margin can be expressed in two ways. These are:
- Margin Requirement
- Required Margin
Margin Requirement
Margin can be expressed as a percentage of the ‘notional value’ or ‘position size’ of your opening position. This percentage is your margin requirement and is why you see margins matched to the derivative you are trading. For example, when trading forex, you may see:
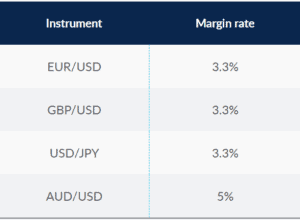
To calculate the margin requirement the following formula is applied
Margin Requirement = 1 / Leverage Ratio
Required Margin
When Margin is expressed in currency, then it is the amount you will need in the currency of your trading account. The required margin is also sometimes called the initial margin, deposit margin, or entry margin. This can be calculated as follows:
When your trading account is the same as the base currency, then your trading account will require the following trading margin:
Required Margin In Trading Account = Notional Value x Margin Required
When your trading account uses a different currency than the base currency, then the requirement for margin will be:
Required Margin In Trading Account = Notional Value x Margin Required x Exchange Rate Between Base Currency and Account Currency
When you close your position and complete the trade, your margin is returned to your account. This is known as ‘freed’ or ‘released’ and can be re-used to open new positions.
Used Margin
One other concept that should be understood when trading is ‘used margin’. If you open multiple trading positions at a time, each position or trade will have its own required margin. Used margin is the total of all required margins for all your positions that are open at one time.
While required margins only require you to have enough funds in your trading account for a particular trade, used margin requires you to have enough deposited in your account to keep all your trades open. This is sometimes called your maintenance margin.
Used Margin = Total amount of margin currently in use to maintain all existing open positions
Free Margin
Free Margin or usable margin is the difference between account equity and used margin.
Free Margin = Account Equity - Used Margin
There are two aspects to free margin, these are:
- Funds available in your trading account to open a new position
- How much funds you have in your account to maintain existing open positions
Margin Level
The margin level is closely related to free margin. Margin level allows you to determine how much you have available to take a new position in your trading account. Margin level is calculated as:
Margin Level = (Equity / Used Margin) x 100%
A good trading platform will calculate and display your margin level. A higher margin level means more free margin available for trading. A lower margin level means your trading account is at risk of debt and can result in a margin call or even stop out.
Margin Call
Your broker will set a margin limit to ensure your account has a safe maintenance level and avoid your account falling below the required margin. This limit will usually be 100% but will vary from broker to broker. A 100% margin level means the account equity is the same as the margin.
In the event your margin level does fall below the broker’s margin limit, then a margin call will be triggered. When a margin call occurs, the broker will ask you to top out your account or close some open positions. You will also not be allowed to open any new positions. If your account margin level continues to fall, then a stop-out will be activated. The broker will attempt to close some or all open positions to bring your trading account back above the margin limit.
Leverage And Margin Are Different
In order to open your position, the broker will list either
- The maximum leverage ratio, or
- The % of margin they require
The two concepts are often used interchangeably as they are based on the same concept. However, they are also different. The margin the broker requires will reflect the leverage you can access. On the flip side, the leverage the broker will allow shows the margin for the deposit the broker will require.
Leverage is the debt you take on to trade positions that are larger than the funds you have in your trading account. Leverage is a ratio between how much you have available to invest and the amount the broker will amplify your investment. This ratio is 1:Leverage. A ratio of 1:500 means that for every $1 you have unused in your trading account, the broker will give you an extra $500.
Leverage = 1 / Margin Requirement
For example, if the margin requirement is 3% then 33 = 1 / .03
As previously discussed, the Margin requirement is how much unused capital you need in your trading account to access leverage. This is expressed as a margin percentage.
Margin Requirement = 1 / Leverage Ratio
If the ratio is 400:1 then 0.25 = 1 / 400
Margin and Leverage have a directly inverse relationship. The below table shows the relationship between leverage and margin.

Brokers can set their own margin requirements but are confined to the conditions of the appropriate financial regulator. All European regulators such as the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and Cyprus Securities Exchange Commission (CySEC), and the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) limit the maximum margin to 3% for major currency pairs and 5% for minor currency pairs when using a retail investor account. Traders that qualify for a professional account will require less margin as regulators consider these forex traders to have the expertise and the funds to cope with any losing positions.
You can view margin levels on our regulator-specific pages such as the ASIC Regulated Brokers or FCA Regulated Brokers and get an idea of trading popularity on our forex by Top Forex Trading Countries guide. We also completed our 2025 guide on the Best Forex Brokers In Australia.
Risks of Margin Trading
While margin trading is a good tool for forex trading to increase profits, it is important to realise that there are risks involved with it. Margin trading means using leverage, and leverage means you are taking on debt. Should movements for currency pairs such as EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY move in an unfavourable direction then your losses can lead to significant debt with your broker.
Forex is a complex financial instrument to master. If you wish to trade on margin, remember that trading is done responsibly. The best way this can be done is by only using the leverage you need for trading and avoiding using leverage to hold larger positions when market volatility is high. It can help to use risk management tools such as Stop Loss Orders, Guaranteed Stop Loss, and negative balance protection to help reduce the chances of incurring losses.
Justin Grossbard
Having traded since 1998, Justin is the CEO and Co-Founded CompareForexBrokers in 2004. Justin has published over 100 finance articles from Forbes, Kiplinger to Finance Magnates. He has a Masters and Commerce degree and has an active role in the fintech community. He has also published a book in 2023 on on investing and trading.



Ask an Expert
what is the best Australian broker for margin trading?
Margin Trading, also known as leverage trading is a way to trade more with less of your own cash. How much margin you can use, will depend on the broker and the regulator the broker is using. All brokers allow you to trade with the maximum leverage permitted by the regulator, this is especially so in Australia, Europe, The UK, the UAE and Singapore where the maximum leverage is quite low. It is countries with less stringent regulators (South Africa, Belize, Seychelles, Vanuatu, New Zealand) or no regulator where differences may occur as these regulators have no maximum leverage.
Is margin trading good for beginners? Sounds complicated
If you are trading CFDs, then you will have no choice but to trade on margin. That said, as a beginner, it is a good idea to start with a demo account and practice and when ready, be conservative with your leverage when using a live account.