What is a Market Maker
Market Makers (aka liquidity providers) provide quotes and take the other side to your trade. Learn what a market maker is in forex and the role they play in making trading possible.
Written by Justin Grossbard
Updated:
- 67 Forex Brokers reviewed by our expert team (See our top 10 picks)
- 50+ years combined forex trading experience
- 14,000+ hours comparing brokers in the past 12 months
- Structured and in-depth evaluation framework (Our Methodology)
Our broker reviews are reader supported and we may receive payment when you click on a partner site. For more information, visit our About Us page.
Table of Contents
Market makers are liquidity providers that continuously provide quotes on both the bid and sell side regardless of their own thoughts on future movements of the asset. When you make a trade, your counterparty, the person on the other side of your trade is the market maker. Market makers go by a number of names such as liquidity provider, dealing desk broker, and B-book broker.
In this guide, we will look at what exactly a market maker is and what it means to trade with a market maker. We will also look at the counterpoint to a market maker, a dealing desk broker, and how trading execution with no dealing desk and dealing desk brokers work.
In this article, we will look at the following:
- What a market maker broker is
- The role of the market maker in trading
- How market makers make money
- What is a market maker broker (dealing desk broker)
- What a dealing desk does when they receive a trading request
- Can you trust a dealing desk broker?
- Advantages and disadvantages of using a dealing desk broker
- Conclusion
What Is A Market Maker?
When you wish to buy or sell a financial instrument such as forex, gold, or cryptocurrencies, chances are high that you will deal with a market maker.
Market makers are the counterparties to your trade. This means when you wish to buy, the market maker will provide a bid quote and if you wish to sell, the market maker will provide an ask (or offer) price. As a major provider of liquidity to the market, market makers will always take the other side of your trade, regardless of whether they believe the trade is likely to be in their interests or not.
As market makers are the counterparty to your trade, they profit when you lose and lose when you profit. So you may sometimes hear them referred to as b-book brokers as they take the other side of the ledger.
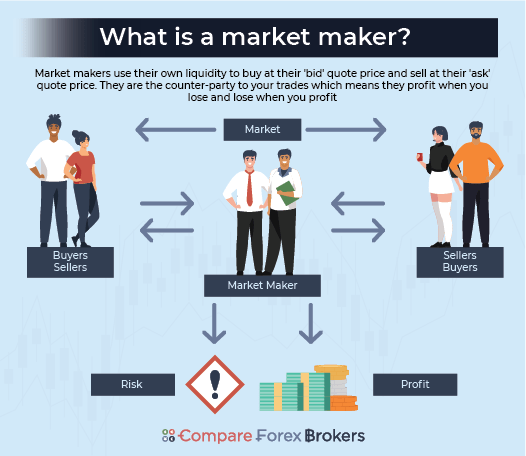
The Role Of The Market Maker
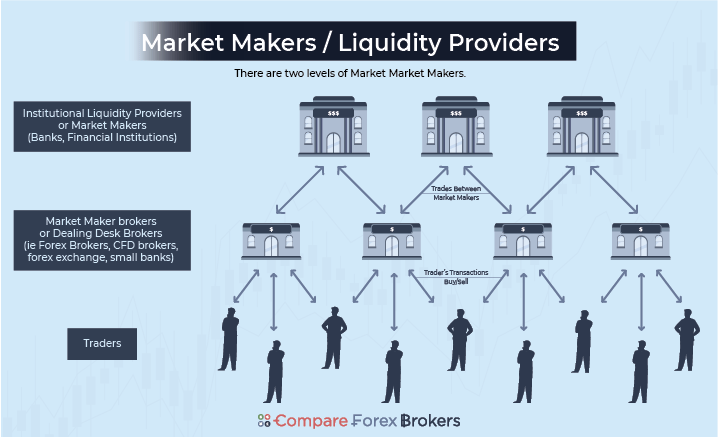
Market makers, which will usually be international banks, financial institutions, multinational corporations, private investors, or brokers, play two important roles that make trading possible.
Market Makers Provide Liquidity To The Market
First, they provide liquidity to the market, so market makers are sometimes called liquidity providers. Liquidity providers help manage the liquidity so that supply meets demand in a timely fashion.
Market Makers Ensure There Will Be A Counterparty
Second, market makers guarantee there will be a counterparty to the trade. Market makers continuously provide buy and sell quotes as long as they have liquidity. Without market makers, assets are likely to be illiquid, as finding someone that has an opposite opinion to your desired trade can be difficult. Market makers will always take the other side of the trade, regardless of whether they think the price will go up or down.
How Market Makers Make And Lose Money
Maker makers are said to ‘make the market’, this is because they set both the bid and ask price for each transaction. They provide their own quotes (usually matched to interbank prices) which allow them to buy at the best ‘bid’ price available and sell at the best price on offer. This difference between the bid-ask (or buy-sell) is known as the spread and provides the broker with their source of profits.
The higher the ask price compared to the bid price, the more profit the market maker gets. This spread compensates for the market maker’s risk they take on with the trade. The market maker will always take the other side, regardless of their opinion of the trade, so they take on a natural risk by being the counterparty when trading with informed traders.
Market makers can also lose money if the market moves against them and they cannot respond to these events fast enough. To protect themselves from crippling losses when the market moves against them, Market makers adopt hedging strategies.
Market Maker Brokers aka Dealing Desk Brokers
In order to make a trade, you will nearly always need to connect with a market maker. This inevitably means using the services of a broker. This broker can either be a dealing desk broker or a no-dealing desk broker.
Dealing Desk (DD) brokers will always be the counterparty to your trades. This means you are dealing directly with them. Even if the dealing desk broker uses another a 3rd party liquidity provider, clients still only deal with the dealing desk broker.
This differs from a no-dealing desk broker who connects professional and retail traders with liquidity providers using execution methods such as electronic communication networks (ECN), Straight-through processing (STP), and direct market access (DMA). Clients of STP or Best ECN Forex Brokers do not deal with the brokers themselves. In a sense, you could call these liquidity providers wholesale or core liquidity providers.
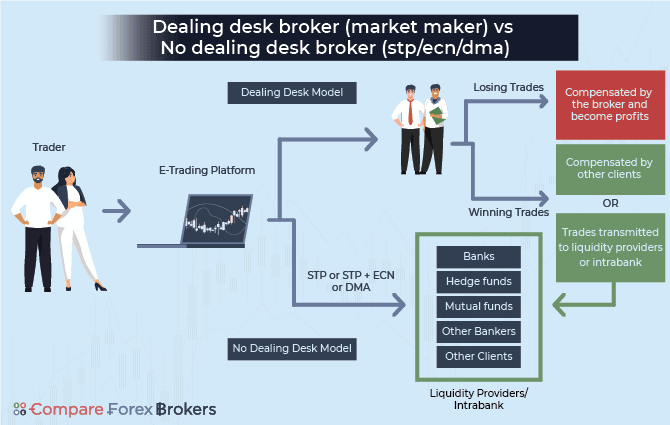
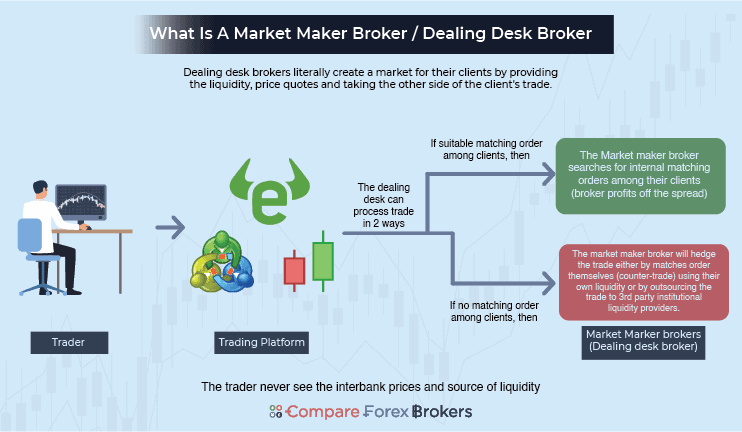
What A Dealing Desk Broker Does When They Receive A Trade Request
Dealing desk brokers can assess all trade requests that come from their clients. From this point, the broker will internalise the transaction or use a 3rd party liquidity provider to complete the trade. You will never know how the broker sources the liquidity to complete your trade.
Dealing Desk Broker Uses Their Own Liquidity
If the broker internalises the transaction, then any of the following will happen:
1. Find a client to use as a counterparty: If existing clients are making buy or sell offers that take the other side, then the broker may use each opposite trade to complete the trade.
2 . Dealing desk brokers will usually opt to complete the trade from their end when:
- Speed is a priority: Using the broker’s own resources may be faster than connecting with a liquidity provider
- The size of the trade is too low: Wholesale liquidity providers don’t find it cost-effective to deal with small positions. Brokers, however, want to attract and keep clients, so will fill this gap
- Save on cost: The broker can save on costs for themselves by using their own liquidity
- Make fixed spreads practical: Wholesale liquidity providers don’t offer fixed spreads. So dealing desk brokers can better control the spread risks for fixed spreads using their own liquidity
3. Dealing desk brokers will send the order to a third market maker when:
- Can’t find a client to internalise the trade: If they can’t find a matching order from the clients, then the broker may engage a liquidity provider
- Lacks liquidity: if the dealing desk lacks liquidity, then they may need to use a liquidity provider
- Large position: If the trader’s position is unusually large, then the dealing desk make not have the liquidity available
- Incentive: In some cases, 3rd party liquidity providers give dealing desk brokers sufficient incentive to use them
When the broker uses a 3rd party market maker or liquidity provider, then the broker is said to be hedging their position.
Can You Trust Market Makers With Their Quotes?
Since market-making brokers provide their own quote and profit when you lose, it is easy to think it is in the interest of these brokers to manipulate spreads in their favour. This doesn’t happen, at least not with brokers using a good regulator.
Reasons market makers’ spreads are not manipulated:
- Regulation: Good Regulators such as FCA (the UK), CySEC (Cyprus), NFA (The US), ASIC (Australia), FSA (Japan) require brokers to offer fair pricing. Tier-3 regulators such as IFSC (Belize), FSB (Bahamas) may not be stringent about this.
- Competition: Competition between brokers is intense, which ensures prices are close to (if not the same as) interbank rates.
- Liquidity Pools: For price integrity, many market makers simply price match or aggregate prices from a liquidity pool.
You can view our Best Forex Brokers In Australia page for the leading brokers regulated by ASIC.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Market Makers
Choosing a market maker broker has some advantages and disadvantages, and it is worth listing these.
Advantages:
1. Commissions are included in the spread
There are two basic types of trading accounts.
- Standard accounts: which are commission-free or rather have commission costs included in the spread
- ECN or Pro accounts: which are spreads plus commission.
Dealing desk brokers offer standard accounts, so while the spreads are wider, it doesn’t mean more trading costs. You will need to compare the dealing desk brokers’ spreads with the spreads of the ECN or Pro accounts and also add their commission costs to determine which type of broker offers lower costs.
While Standard accounts may cost slightly more, beginner brokers and long-term traders may consider the lack of commission an advantage because of their simpler cost structure.
2. Spreads can be fixed or variable
Market makers can offer fixed or variable spreads. It would be highly unusual for no dealing desk brokers to offer fixed spreads.
Market prices are constantly changing, so core liquidity providers don’t benefit from taking on the risk of offering fixed spreads. Dealing desk brokers, however, may be prepared to take on the risk of attracting clients that prefer a trading strategy of stable prices during times of market volatility.
3. Wider choice of products
Dealing desk brokers commonly offer more products beyond the most popular product common among most brokers. While nearly all brokers offer popular CFDs like forex currency pairs such as EUR/USD, indices, gold, silver, and cryptocurrencies, you may find dealing desk brokers offer the less common options such as bonds, interest rates, futures, options, and sectors. You may also find they offer more variety of these products such as forex cross pairs like GBP/AUD and exotics.
4. Offers more features – risk management, education
Dealing desk brokers usually have more comprehensive trading experience than no-dealing desk brokers. Features dealing desk brokers commonly offer include:
- Their own in-house trading platform: designed especially for their clients. No dealing desk brokers use mainstream platforms like cTrader, MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, and Webtrader.
- Extensive risk management: tools to better manage the high risk of trading such as guaranteed stop loss
- Education libraries: Sometimes available for free, these cover topics such as online trading, trading forex, and trading strategies
5. No minimum deposits
Many no-dealing desk brokers usually have a minimum deposit requirement to open an account, even if it’s just $1. Dealing desk brokers rarely have a minimum deposit.
Disadvantages
1. Conflict of interest
As dealing with desk brokers is your counterparty, they have a natural conflict of interest since they profit when you lose. While most dealing desk brokers operate with integrity, it is something to keep in mind.
2. Lack of transparency – can’t see interbank prices
As the dealing desk broker acts as the middleman between the trader and liquidity pools, you will not have visibility of the interbank prices quoted by the liquidity providers.
3. May not accept all positions or provide re-quotes
Dealing desk brokers may reject your trade or offer a revised quote (known as a re-quote).
For example, if the dealing desk broker is aware the trade is very large and highly profitable, they may scrutinise the trade more closely. The broker can either process the order internally, hand over the order to an external liquidity provider, or reject the order.
4. Artificial quotes
Dealing desk brokers make their own market so can set their own prices. While these prices are usually aligned with interbank prices, they are still set by the broker.
5. Spreads are wider
Wider spreads can mean more trading costs. If you are a frequent trader, you are likely to prefer a commission-based trading account.
6. Scalpers are often not welcome
Dealing desk brokers lose money when you profit, so don’t benefit from scalping practices where traders aim for small profits with multiple trades.
7. Social trading tools not usually available
Many dealing desk brokers have proprietary trading platforms that don’t allow integration with 3rd party products that are not made by the broker. For this reason, most social trading tools cannot be used with dealing desk brokers’ trading platforms.
8. Proprietary trading platforms
While a good trading platform designed for the needs of the broker’s clients can be a strength, it can also be a weakness. Many brokers design their trading platforms so that only their clients can use them to lock them into their ecosystem. This can make it hard to leave the broker should you wish to sign up with a new forex broker or crypto broker.
Conclusion
Market makers play a critical role in making trading possible. Without them, it’s difficult to find a party with liquidity that will take the other side of your trade.
When choosing a broker for forex trading, you have a choice of a dealing desk broker or a no-dealing desk broker. The former is nearly always a market maker, while the latter offers ECN, STP, or DMA-style pricing.
This article looks at how a market maker works when trading forex and what features Market Maker forex brokers offer. Market makers have several advantages but also have some disadvantages. Certainly, you will find market maker brokers have features you won’t find with an ECN-style broker. No-dealing desk brokers remain a popular choice. With the article, you should have a good understanding of market makers and why you might choose to use a market maker forex broker.
Justin Grossbard
Having traded since 1998, Justin is the CEO and Co-Founded CompareForexBrokers in 2004. Justin has published over 100 finance articles from Forbes, Kiplinger to Finance Magnates. He has a Masters and Commerce degree and has an active role in the fintech community. He has also published a book in 2023 on on investing and trading.



Ask an Expert
Is a market maker or ECN broker better?
This depends on what you are looking for in a broker. ECN brokers tend to be cheaper (even with the commission costs included) but it depends on the broker. ECN style brokers also tend to be a better option for scalpers and social traders. Market Makers often offer features not always available with ECN brokers such as extra risk management tools (ie. guaranteed stop loss), fixed spreads, proprietary trading platforms that have features not found on metatrader, more trading products and larger education libraries. Theoretically, Market Makers can also have faster execution speed.